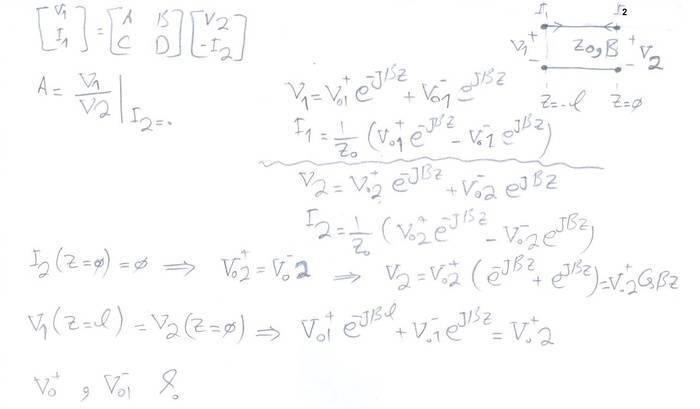SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on deriving the ABCD matrix for a transmission line, specifically how to determine the A element value and the reflection coefficient ρ at position 1. The relationship between the forward and backward traveling voltages (V(1)+ and V(1)-) is crucial for this derivation. The reflection coefficient can be calculated using the formula Γ2 = (Z2 - Z0)/(Z2 + Z0), where Z0 is the characteristic impedance. The final equations for the voltages and currents are expressed as V1 = AV2 + BI2 and I1 = CE2 + DI2, where A, B, C, and D are functions of θ and Z0.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of transmission line theory
- Familiarity with the ABCD parameters
- Knowledge of reflection coefficients in electrical engineering
- Basic concepts of complex impedance and phasors
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the ABCD parameters for different transmission line configurations
- Learn how to calculate the reflection coefficient in various scenarios
- Explore the use of complex numbers in analyzing AC circuits
- Investigate the impact of load impedance on transmission line performance
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, students studying transmission line theory, and professionals involved in RF design or telecommunications will benefit from this discussion.