- #1
Minghan
- 17
- 2
- TL;DR Summary
- Is there any method to measure the power of the pump?
Want to know how to get the actual power the pump needs.
I can measure the flow rate by the flow meter and count the revolutions of the pump.
But selecting the proper motor for the pump would be a problem.
So I want to know how to determine the power of the rotary lobe pump and generate the graph like below.
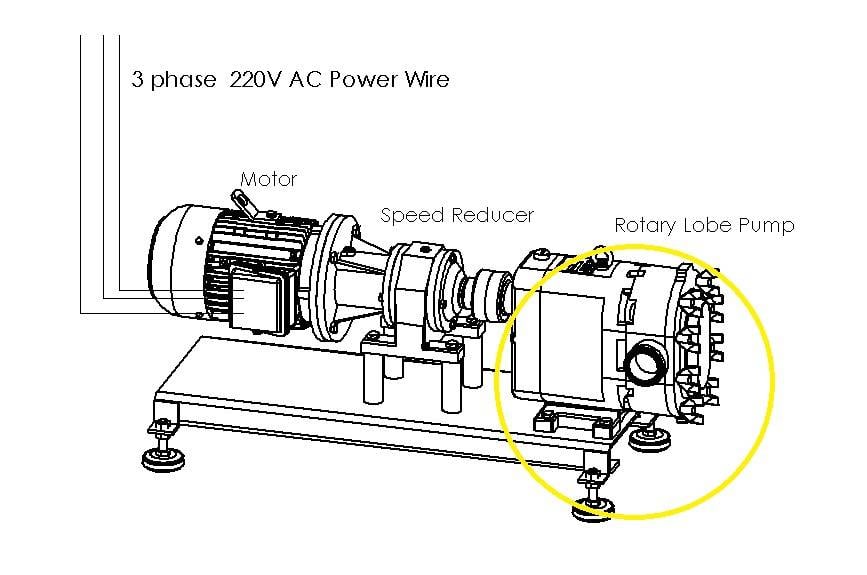
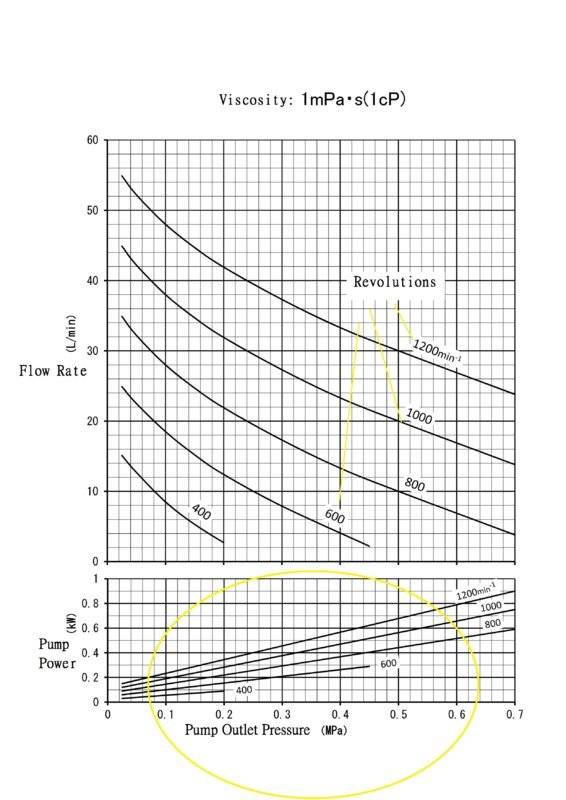

I can measure the flow rate by the flow meter and count the revolutions of the pump.
But selecting the proper motor for the pump would be a problem.
So I want to know how to determine the power of the rotary lobe pump and generate the graph like below.