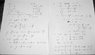Homework Help Overview
The problem involves finding the area of quadrilateral BEFC within an equilateral triangle ABC, where specific points are defined based on the triangle's geometry and extensions. The triangle has sides of 2 cm, and additional points D and E are introduced, with line segments intersecting at point F.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss various methods for determining the area, including the use of the Pythagorean theorem and coordinate geometry. Some suggest finding coordinates for points and using line equations, while others propose leveraging geometric properties and theorems related to medians in triangles.
Discussion Status
The discussion includes multiple approaches to the problem, with some participants sharing their attempts and others suggesting alternative methods. There is a recognition of geometric properties that could simplify the solution, though no consensus on a single method has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the potential complexity of using coordinates and express interest in simpler geometric approaches. There is also mention of varying educational experiences regarding geometry concepts, which may influence understanding and problem-solving strategies.