Discussion Overview
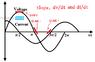
The discussion revolves around the behavior of current in an AC capacitive circuit, particularly at the moment when the voltage across the capacitor is zero. Participants explore the implications of current leading voltage in this context, questioning how current can be at its maximum when the EMF is zero and the capacitor is uncharged.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions how current can be maximum at t=0 when the voltage is zero, suggesting a lack of energy to push electrons.
- Another participant asks for clarification on the circuit configuration, hinting at the importance of defining the circuit more clearly.
- A participant mentions the assumption of zero equivalent resistance in their studies, raising questions about the effects of capacitive reactance.
- It is proposed that the voltage source supplies energy to drive the current waveform, with maximum current occurring when the voltage is changing most rapidly.
- One participant points out that t=0 and ωt=2πn for n>0 are not equivalent, indicating that current does not necessarily flow at t=0.
- A participant explains that the current through a capacitor is the derivative of the voltage across it, emphasizing that maximum current occurs at the zero crossing of the voltage waveform.
- Another participant discusses the implications of assuming a switch in the circuit and how that affects the interpretation of t=0 in steady-state AC graphs.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the interpretation of current and voltage relationships in AC circuits, particularly at the moment of zero voltage. There is no consensus on the implications of these relationships, and the discussion remains unresolved.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that the behavior of AC circuits, particularly with sine waves, can be counterintuitive and that transient behaviors may complicate the understanding of current and voltage at specific moments.