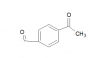
SUMMARY
Acetaldehyde is not a strong nucleophile for aromatic nucleophilic substitution due to its electron-withdrawing nature. The discussion highlights the challenges of using acetaldehyde in reactions with non-activated aromatic compounds. Participants emphasize the importance of the aromatic system's electron density and suggest that preserving the aldehyde functionality may complicate the substitution process. pKa data for acetaldehyde is also requested to better understand its reactivity in this context.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of aromatic nucleophilic substitution mechanisms
- Knowledge of pKa values and their relevance to nucleophilicity
- Familiarity with electron-rich and electron-poor aromatic systems
- Basic concepts of aldehyde reactivity in organic chemistry
NEXT STEPS
- Research the mechanisms of aromatic nucleophilic substitution in detail
- Investigate pKa values of acetaldehyde and other aldehydes
- Explore strategies for enhancing nucleophilicity in aromatic systems
- Study the effects of substituents on the reactivity of aromatic compounds
USEFUL FOR
Chemists, organic synthesis researchers, and students studying nucleophilic reactions in aromatic compounds will benefit from this discussion.