SUMMARY
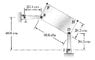
The discussion focuses on determining the instantaneous center of rotation for a bar AB with a constant angular velocity of 25 rad/s counterclockwise. The user successfully calculated the velocity of point B (Vb) as 507.5j using the equation Va = Vb + Wba x Ra/b. However, they expressed uncertainty about applying the instantaneous center of rotation method to find the required values for the rectangular plate FBDH and point F. Participants in the discussion provided guidance on identifying the motion directions of points B and D to aid in the solution.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of angular velocity and its implications in rigid body motion
- Familiarity with the equation Va = Vb + Wba x Ra/b
- Knowledge of instantaneous centers of rotation in kinematics
- Basic principles of vector addition in two-dimensional motion
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of instantaneous centers of rotation in rigid body dynamics
- Learn how to apply the equation Va = Vb + Wba x Ra/b in various scenarios
- Explore examples of angular velocity calculations in mechanical systems
- Investigate the relationship between linear and angular motion in rigid bodies
USEFUL FOR
Students in mechanical engineering, physics enthusiasts, and professionals working with kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies will benefit from this discussion.