chavic
- 9
- 0
[SOLVED] Last 3 problems on Rotational Dynamics
OK, I've done problems 1-3, but I'm having a real hard time with 4-6. Any help you guys could give me would be greatly appreciated!
4. Homework Statement
A block of mass m1 = 2.45 kg and a block of mass m2 = 5.55 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the shape of a solid disk having radius R = 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. These blocks are allowed to move on a fixed block-wedge of angle θ = 30.0°. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Draw free-body diagrams of both blocks and of the pulley.
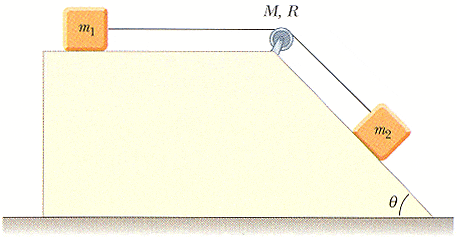
(a) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks.
(b) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley.
Left:
Right:
4. Relevant equations
\sum\tau=RFsin\theta
net \tau=I\alpha
I=.5MR^{2}
\alpha= a/R
4. The attempt at a solution
I drew a Free Body Diagram and used the given information to find that:
This is wrong and I tried several different times, went over my work and I can't find what I did wrong.
5. Homework Statement
Two blocks, as shown below, are connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a pulley of radius 0.320 m and moment of inertia I. The block on the frictionless incline is moving up with a constant acceleration of 1.20 m/s2.
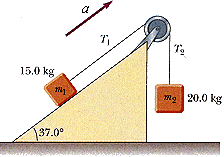
(a) Determine the tensions in the two parts of the string.
T1:
T2:
(b) Find the moment of inertia of the pulley.
5. Relevant equations
?
5. The attempt at a solution
6. Homework Statement
The reel shown below has radius R and moment of inertia I. One end of the block of mass m is connected to a spring of force constant k, and the other end is fastened to a cord wrapped around the reel. The reel axle and the incline are frictionless. The reel is wound counterclockwise so that the spring stretches a distance d from its unstretched position and is then released from rest.
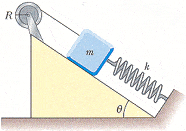
a) Find the angular speed of the reel when the spring is again unstretched. (Answer using theta for θ, g for the acceleration due to gravity, and R, I, m, k, and d, as necessary.)
(b) Evaluate the angular speed numerically at this point if I = 1.20 kg·m2, R = 0.300 m, k = 50.0 N/m, m = 0.500 kg, d = 0.200 m, and θ = 37.0°.
6. Relevant equations
?
6. The attempt at a solution
OK, I've done problems 1-3, but I'm having a real hard time with 4-6. Any help you guys could give me would be greatly appreciated!
4. Homework Statement
A block of mass m1 = 2.45 kg and a block of mass m2 = 5.55 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the shape of a solid disk having radius R = 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. These blocks are allowed to move on a fixed block-wedge of angle θ = 30.0°. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Draw free-body diagrams of both blocks and of the pulley.
(a) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks.
(b) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley.
Left:
Right:
4. Relevant equations
\sum\tau=RFsin\theta
net \tau=I\alpha
I=.5MR^{2}
\alpha= a/R
4. The attempt at a solution
I drew a Free Body Diagram and used the given information to find that:
m_{1}=2.45 kg
m_{2}=5.55 kg
\mu=.36
R=.25 m
M=10 kg
\theta=30
n_{1}=24.01 N
n_{2}=47.1031
Force of Friction on M1=8.6436 N
Force of Friction on M2=16.9571 N
M1gsin\theta=27.195
- So some of forces acting on pulley is 1.5943 N to the right
- So \sum\tau=RFsin\theta
=.398575
- Plug this into net \tau=I\alpha
(I=.5MR^{2})
(I=.3125)
.398575=.3125\alpha
1.27544=\alpha
- Plug this into \alpha= a/R
1.27544=a/.25
.31886=a
This is wrong and I tried several different times, went over my work and I can't find what I did wrong.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5. Homework Statement
Two blocks, as shown below, are connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a pulley of radius 0.320 m and moment of inertia I. The block on the frictionless incline is moving up with a constant acceleration of 1.20 m/s2.
(a) Determine the tensions in the two parts of the string.
T1:
T2:
(b) Find the moment of inertia of the pulley.
5. Relevant equations
?
5. The attempt at a solution
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6. Homework Statement
The reel shown below has radius R and moment of inertia I. One end of the block of mass m is connected to a spring of force constant k, and the other end is fastened to a cord wrapped around the reel. The reel axle and the incline are frictionless. The reel is wound counterclockwise so that the spring stretches a distance d from its unstretched position and is then released from rest.
a) Find the angular speed of the reel when the spring is again unstretched. (Answer using theta for θ, g for the acceleration due to gravity, and R, I, m, k, and d, as necessary.)
(b) Evaluate the angular speed numerically at this point if I = 1.20 kg·m2, R = 0.300 m, k = 50.0 N/m, m = 0.500 kg, d = 0.200 m, and θ = 37.0°.
6. Relevant equations
?
6. The attempt at a solution