SUMMARY
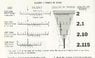
The least count of a vernier caliper is defined as the difference between one Main Scale Division (MSD) and one Vernier Scale Division (VSD), known as the Vernier Constant. For a vernier caliper with 49 divisions on the main scale, each measuring 0.025", and 25 divisions on the vernier scale, the resolution achieved is 0.001". The principle behind the vernier scale, established by Pierre Vernier in 1631, allows for precise measurements by aligning the divisions of the vernier with the main scale. The Gage Makers Rule of Ten is also referenced as a method to minimize measurement errors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Main Scale Division (MSD) and Vernier Scale Division (VSD)
- Familiarity with the concept of Vernier Constant
- Basic knowledge of measurement precision and accuracy
- Awareness of historical context regarding measurement tools
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mathematical principles behind the Vernier scale
- Learn about the Gage Makers Rule of Ten and its application in measurement
- Explore the differences between accuracy and precision in measurement tools
- Investigate the evolution of measuring instruments from historical perspectives
USEFUL FOR
Engineers, precision measurement technicians, and students in fields requiring accurate measurement techniques will benefit from this discussion on vernier calipers and their operational principles.