MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here is the question:
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can view my work.
Find the local maximum and minimum values and saddle point(s) of the function. If you have three-dimensional g?
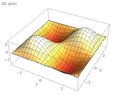
Find the local maximum and minimum values and saddle point(s) of the function. If you have three-dimensional graphing software, graph the function with a domain and viewpoint that reveal all the important aspects of the function. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.)
f(x, y) = 3 sin x sin y, −π < x < π, −π < y < π
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can view my work.