dmaling1
- 2
- 0
This is a two part question. I completed the 1st part, but I am having a difficult time on the second part. I have one try remaining.
Magnetic Field and Poynting Flux in a Charging Capacitor-
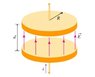
When a circular capacitor with radius and plate separation is charged up, the electric field , and hence the electric flux , between the plates changes. According to Ampère's law as extended by Maxwell, this change in flux induces a magnetic field that can be found from
integral of B * dl = Mu 0 (i + Epsilon 0 (delta flux/delta t)) = ampere maxwell law
We can solve this equation to obtain the field inside a capacitor:
B(r) = Mu 0 (ir/2piR^2) theta
where r is the radial distance from the axis of the capacitor.
Part A.) Find an expression for the magnitude of the Poynting vector S on the surface that connects the edges of the two circular plates.
S = 1/Mu 0 (E X B) = S(t) = (i^2/(2pi^2R^3epsilon 0))t
Part B.) Calculate the the total amount of energy U that flows into the space between the capacitor plates from t= 0 to t= T, by first integrating the Poynting vector over the surface that connects the edges of the two circular plates, and then integrating over time.
Here is where I am unsure where to go.
I believe we will need to integrate S*Area, where the area is 2piRd, twice like they said, once respecting to the d distance, and again w/ respect to time. I am having a tough time with the setup, and which we are constants/variables in the integration.
Thanks in advance
Magnetic Field and Poynting Flux in a Charging Capacitor-
When a circular capacitor with radius and plate separation is charged up, the electric field , and hence the electric flux , between the plates changes. According to Ampère's law as extended by Maxwell, this change in flux induces a magnetic field that can be found from
integral of B * dl = Mu 0 (i + Epsilon 0 (delta flux/delta t)) = ampere maxwell law
We can solve this equation to obtain the field inside a capacitor:
B(r) = Mu 0 (ir/2piR^2) theta
where r is the radial distance from the axis of the capacitor.
Part A.) Find an expression for the magnitude of the Poynting vector S on the surface that connects the edges of the two circular plates.
S = 1/Mu 0 (E X B) = S(t) = (i^2/(2pi^2R^3epsilon 0))t
Part B.) Calculate the the total amount of energy U that flows into the space between the capacitor plates from t= 0 to t= T, by first integrating the Poynting vector over the surface that connects the edges of the two circular plates, and then integrating over time.
Here is where I am unsure where to go.
I believe we will need to integrate S*Area, where the area is 2piRd, twice like they said, once respecting to the d distance, and again w/ respect to time. I am having a tough time with the setup, and which we are constants/variables in the integration.
Thanks in advance