captainhampto
- 12
- 0
Hey guys,
I'm attempting to map some discrete points on the surface of the Bloch sphere:
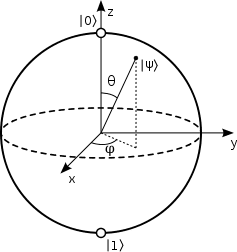
For instance, the full spectrum of ranges for variable theta is 0 < theta < pi. However, my goal is to limit that range from some theta_1 < theta < theta_2. I was going to use a spherical harmonic technique to limit the ranges, but my question is this:
If I do succeed in limiting the ranges, will this actually map to these new points (theta_1 and theta_2) or will it simply alter the probability of the qubit represented by the Bloch sphere to collapsing to either basis state of 0 or 1?
My main goal is to have some value between theta_1 and theta_2 arise from this technique so that I do not get the full spectrum of 0 to pi. If a better technique exists I would be most obliged to learn of it.
If any further clarification is needed, please do not hesitate to post a response, as perhaps I am leaving out some detail that is crucial. Either way, thanks and looking forward to some responses.
I'm attempting to map some discrete points on the surface of the Bloch sphere:
For instance, the full spectrum of ranges for variable theta is 0 < theta < pi. However, my goal is to limit that range from some theta_1 < theta < theta_2. I was going to use a spherical harmonic technique to limit the ranges, but my question is this:
If I do succeed in limiting the ranges, will this actually map to these new points (theta_1 and theta_2) or will it simply alter the probability of the qubit represented by the Bloch sphere to collapsing to either basis state of 0 or 1?
My main goal is to have some value between theta_1 and theta_2 arise from this technique so that I do not get the full spectrum of 0 to pi. If a better technique exists I would be most obliged to learn of it.
If any further clarification is needed, please do not hesitate to post a response, as perhaps I am leaving out some detail that is crucial. Either way, thanks and looking forward to some responses.