Baynie
- 2
- 1
Hello everyone,
For weeks I have been struggling with this quantum mechanics homework involving writing a code to determine the energy spectrum and eigenvalues for the stationary Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator. I can't find any resources anywhere. If anyone could help me get started, get my matrices and equations set up, or has worked a similar problem/written a similar code before, any help would be greatly appreciated! Thanks in advance!

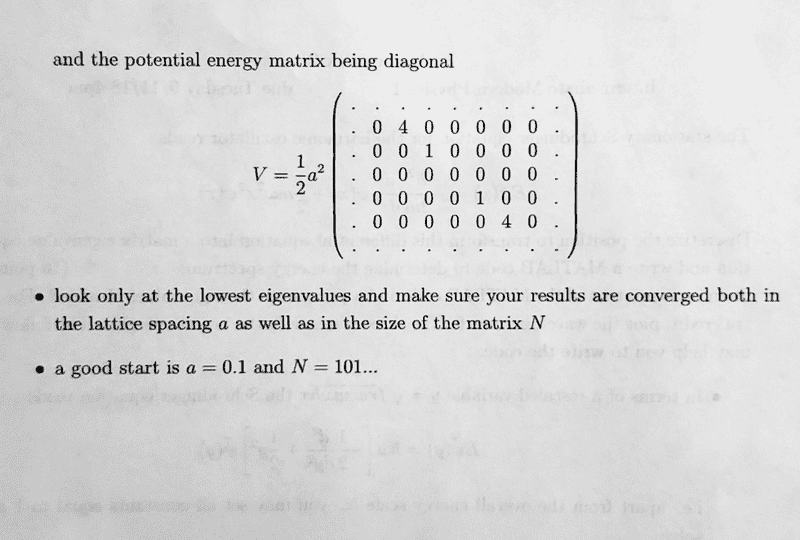
Included in image above
Her is the code I have written so far. I'm not sure if this is even close or on the right track
% Stationary Schrödinger Equation - QHO
clear
clc
hbar = 6.58E-16;
f = 400E-9;
w = 2*pi*f;
m = 1;
N = 101;
a = 0.1;
n = 1:N;
r = n*a;
l = 1;
x = a;
mwhbar = m*w*hbar;
y = r;
% Operators (Matrices)
T = diag(-1*ones(1,N-2),2) + diag(2*ones(1,N-1),1) + diag(-1*ones(1,N),0);
K = (1/(2*a^2)) * T; % Kinetic Energy Matrix
Veff = -(1./r) + l*(l + 1)./(2*(r.^2));
V = diag(Veff);
U = (1/(2*a^2)) * V; % Potential Energy Matrix
% Equations
H = -(1/2*a^2)*(eigen_f(n+1) - 2 * eigen_f(n) * eigen_f(n-1));
For weeks I have been struggling with this quantum mechanics homework involving writing a code to determine the energy spectrum and eigenvalues for the stationary Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator. I can't find any resources anywhere. If anyone could help me get started, get my matrices and equations set up, or has worked a similar problem/written a similar code before, any help would be greatly appreciated! Thanks in advance!
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
Included in image above
The Attempt at a Solution
Her is the code I have written so far. I'm not sure if this is even close or on the right track
% Stationary Schrödinger Equation - QHO
clear
clc
hbar = 6.58E-16;
f = 400E-9;
w = 2*pi*f;
m = 1;
N = 101;
a = 0.1;
n = 1:N;
r = n*a;
l = 1;
x = a;
mwhbar = m*w*hbar;
y = r;
% Operators (Matrices)
T = diag(-1*ones(1,N-2),2) + diag(2*ones(1,N-1),1) + diag(-1*ones(1,N),0);
K = (1/(2*a^2)) * T; % Kinetic Energy Matrix
Veff = -(1./r) + l*(l + 1)./(2*(r.^2));
V = diag(Veff);
U = (1/(2*a^2)) * V; % Potential Energy Matrix
% Equations
H = -(1/2*a^2)*(eigen_f(n+1) - 2 * eigen_f(n) * eigen_f(n-1));

