Stephanus
- 1,316
- 104
Dear PF Forum,
I'm sorry if I ask the basic question here again. Just need confirmation.
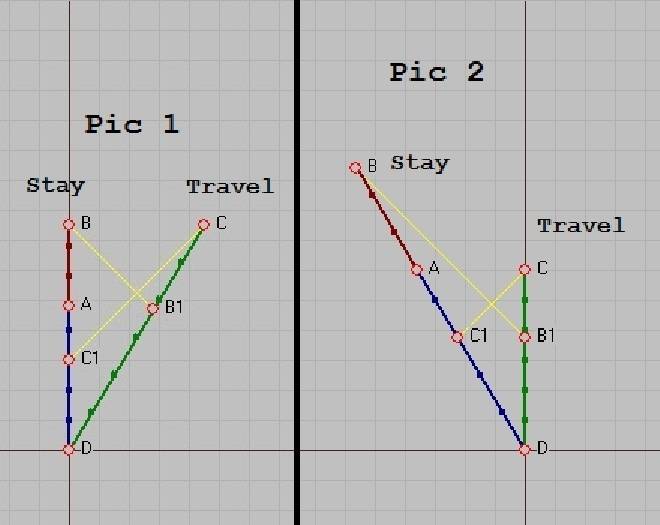
V = 0.6; Gamma = 1.25
TRAVEL travels at 0.6c. STAY stays.
Pic 02 is Pic 01 boosted -V.
1. All STAY knows about TRAVEL is:
Proper Time
Speed
Is this true? And mutually for TRAVEL
2. At B (and C) all STAY knows about TRAVEL proper distance is the distance at B1 (and C1 distance for C).
3 . At B, STAY never knows about C. And C never knows about B. Is this true?
4. It is not relevant for STAY to calculate TRAVEL clock/calendar
For example:
At B, supposedly 1st January 2015; 10:00 AM, there's no need for STAY to calculate when is B1, because there is no certainity/assurance that at start STAY and TRAVEL clocks were synchronized.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In short what STAY knows about TRAVEL?
A. Proper Time
B. Speed
C. Distance (late by the time that light takes to travel from TRAVEL to STAY, for example B can only calculate proper distance from B1 to STAY. STAY's X coordinate always zero, right)
D. Red/Blue shifted. But it's already known right. How can we know proper time and speed if we don't know about Red/Blue shifted.
E. Anything else?
Thanks for any answers.
I'm sorry if I ask the basic question here again. Just need confirmation.
V = 0.6; Gamma = 1.25
TRAVEL travels at 0.6c. STAY stays.
Pic 02 is Pic 01 boosted -V.
1. All STAY knows about TRAVEL is:
Proper Time
Speed
Is this true? And mutually for TRAVEL
2. At B (and C) all STAY knows about TRAVEL proper distance is the distance at B1 (and C1 distance for C).
3 . At B, STAY never knows about C. And C never knows about B. Is this true?
4. It is not relevant for STAY to calculate TRAVEL clock/calendar
For example:
At B, supposedly 1st January 2015; 10:00 AM, there's no need for STAY to calculate when is B1, because there is no certainity/assurance that at start STAY and TRAVEL clocks were synchronized.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In short what STAY knows about TRAVEL?
A. Proper Time
B. Speed
C. Distance (late by the time that light takes to travel from TRAVEL to STAY, for example B can only calculate proper distance from B1 to STAY. STAY's X coordinate always zero, right)
D. Red/Blue shifted. But it's already known right. How can we know proper time and speed if we don't know about Red/Blue shifted.
E. Anything else?
Thanks for any answers.
