phyti
- 452
- 8
I don't remember seeing this solution to the question.
Imagine an object of length d with a reflector on the far end (x=4).
A moves past the object at speed a, emitting a signal at the origin in the positive x direction. A makes one pass in the +x direction, reverses and makes one pass in the -x direction.
Relative to U, with c=1, a=.4:
time out is the same for both passes, t0=d/c.
return time-pass 1, t1=t0(1-a)/(1+a)
return time-pass 2, t2=t0(1+a)/(1-a)
with time dilation for A;
total time-pass 1, T1=2t0*sqrt ((1-a)/(1+a))
total time-pass 2, T2=2t0*sqrt ((1+a)/(1-a))
t0=.5sqrt(T1*T2)
Example:
d=.5sqrt(5.24*12.16) = 4.0
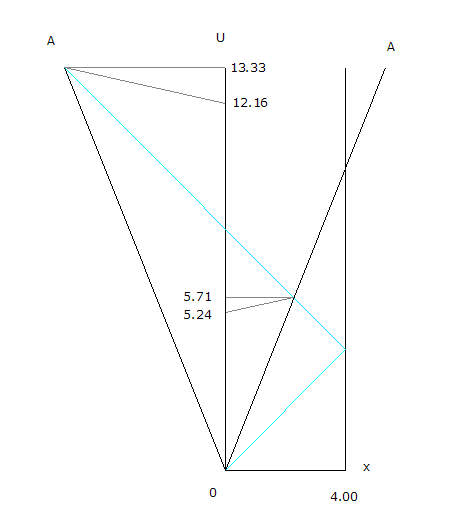
Imagine an object of length d with a reflector on the far end (x=4).
A moves past the object at speed a, emitting a signal at the origin in the positive x direction. A makes one pass in the +x direction, reverses and makes one pass in the -x direction.
Relative to U, with c=1, a=.4:
time out is the same for both passes, t0=d/c.
return time-pass 1, t1=t0(1-a)/(1+a)
return time-pass 2, t2=t0(1+a)/(1-a)
with time dilation for A;
total time-pass 1, T1=2t0*sqrt ((1-a)/(1+a))
total time-pass 2, T2=2t0*sqrt ((1+a)/(1-a))
t0=.5sqrt(T1*T2)
Example:
d=.5sqrt(5.24*12.16) = 4.0