MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here is the question:
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can see my work.
CALCULUS!? A point P needs to be located somewhere on the line AD so that the total...?
Pplease help me with this question, I don't understand how to get an answer :(
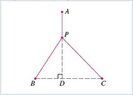
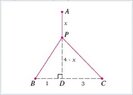
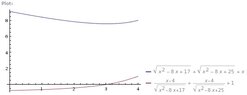
A point P needs to be located somewhere on the line AD so that the total length L of cables linking P to the points A, B, and C is minimized (see the figure). Express L as a function of x = |AP| and use the graphs of L and dL/dx to estimate the minimum value of L. (Round your answer to two decimal places. Assume that |BD| = 1 m, |CD| = 3 m, and |AD| = 4 m.)
View attachment 1718
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can see my work.