- #1
Kile
- 12
- 0
1. The illustrated structure is affected by a known couple, and try to figure out the restraining reaction force of the hinge A and hinge E.
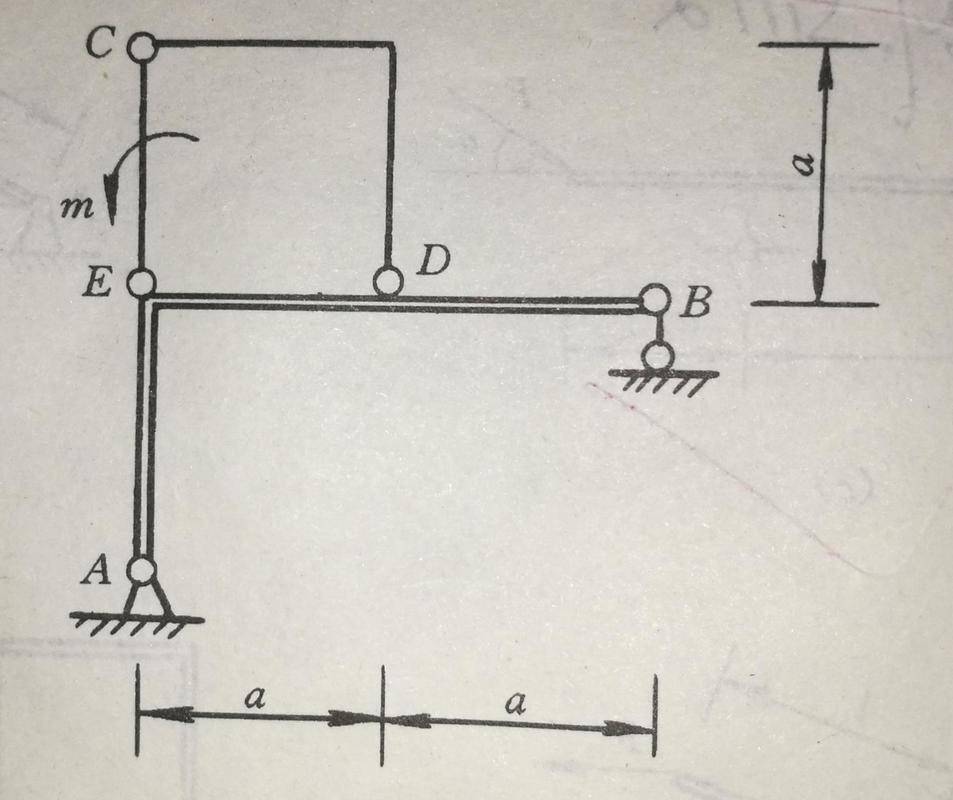
We should analyse ECD instead. Since arm CD is a two force members, so N(C) in in the direction where CD connects by these two points. The distance from E to diagonal CD is a/√2. So we have N(C)=√2 m/a. Because N(C)=N(E) ( N(C) and N(E) together form a couple), N(E)=√2 m/a.
Where did I go wrong?
We should analyse ECD instead. Since arm CD is a two force members, so N(C) in in the direction where CD connects by these two points. The distance from E to diagonal CD is a/√2. So we have N(C)=√2 m/a. Because N(C)=N(E) ( N(C) and N(E) together form a couple), N(E)=√2 m/a.
Where did I go wrong?