milkism
- 118
- 15
- Homework Statement
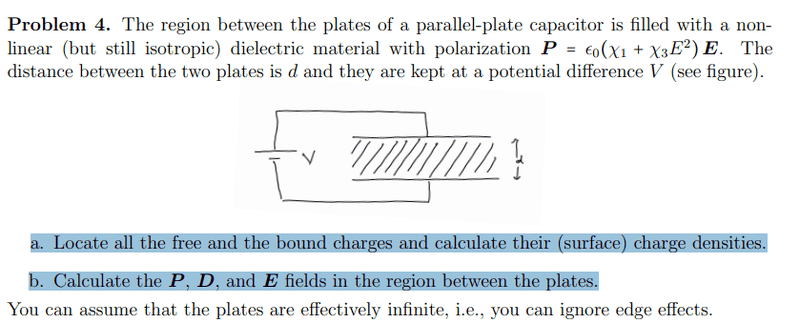
- a. Identify the location of all the free and bound charges present in the region between the plates of the parallel-plate capacitor, and determine the surface charge densities associated with them.
b. Determine the values of the polarization (P), electric displacement (D), and electric field (E) in the region between the plates.
- Relevant Equations
- See solution.
Question:
Solution first part:

Have I done it right?
I don't know how to begin with second part since the dielectric is non-lineair, and most formulas like $$
D=\epsilon E$$ and $$P= \epsilon_0 \xhi_e E$$, only apply for lineair dielectrics. What to do?
Solution first part:
Have I done it right?
I don't know how to begin with second part since the dielectric is non-lineair, and most formulas like $$
D=\epsilon E$$ and $$P= \epsilon_0 \xhi_e E$$, only apply for lineair dielectrics. What to do?