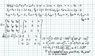- #1
s3a
- 818
- 8
Homework Statement
Obtain the extremum of f(x,y,z) = 2x^2 + y^2 + 2z^2 + 2xy + 2xz + 2y + x - 3z - 5 and determine its nature.
Homework Equations
Partial differentiation and systems of equations.
The Attempt at a Solution
My attempt is attached. In addition to confirming if what I did so far is correct, I would appreciate it if someone could also tell me how to "find the nature" of the point. I believe that means to state if it's a minimum, maximum or saddle point. For a function of two variables, I would know what to do but for a function of three variables, I do not. I remember hearing that we are not responsible for figuring out the nature of points higher than two variables using the method I would use which is the [f_(xy)]^2 - f_(xx) * f_(yy) test but that we should be able to do such a problem using a different easier method. I'm in a Calculus 3 course.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Thanks in advance!