Discussion Overview
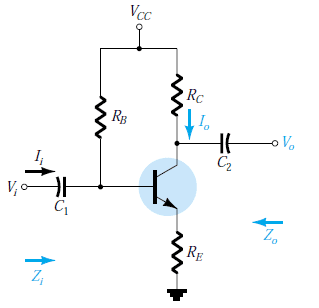
The discussion revolves around the behavior of current in a transistor circuit, specifically addressing why the output current (Io) flows through resistor Rc but not through capacitor C2. Participants explore concepts related to AC and DC current, circuit analysis, and the role of capacitors in the circuit.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest that C2 is open circuited, which would prevent current from flowing through it.
- Others propose that the input current (Ii) is not zero due to the presence of capacitor C1, which is assumed to block DC gain.
- It is noted that Io is defined as the AC current through Rc, and that the current will only flow through the capacitor when the voltage across it changes.
- One participant mentions that the circuit is designed to amplify an AC signal, with components affecting the gain.
- There is a suggestion that Io may be incorrectly marked in the schematic, possibly indicating current through C2 to an unspecified load.
- Another participant emphasizes that DC does not pass through capacitors, which may explain why Io does not go through C2.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express various viewpoints on the behavior of current in the circuit, with no clear consensus on the implications of the circuit design or the role of the components involved. Disagreements exist regarding the interpretation of current flow and the conditions under which it occurs.
Contextual Notes
Some participants mention the need for specific conditions, such as Iin = 0 or Iout = 0, when calculating input or output impedance, but the reasons for these conditions remain unresolved.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be of interest to students studying circuit analysis, particularly those dealing with transistor circuits and the behavior of capacitors in AC and DC contexts.