Karagoz
Assume a person is at space, and assume there's no friction or gravitational force in that space.
The person has a bow and arrow. He stretches the arrow on the bow, and then shots the arrow out in the space. Since there are no friction and gravitational force in that space, the arrow will have constant velocity very long distance or until another force exerted on it.
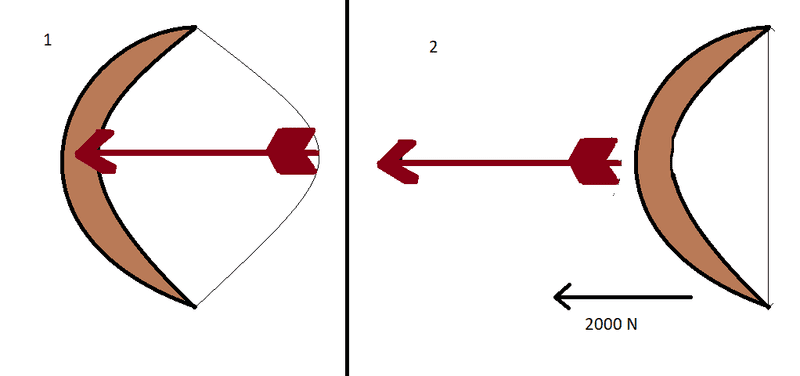 The force exerted on the arrow from the bow is 2000 N. The force is exerted only for 0.05 seconds since the arrow quickly moves out off the bow. And the arrow weights 0.5 Kg. From my calculations* the velocity of the arrow will be 200m/s if I'm not wrong.
The force exerted on the arrow from the bow is 2000 N. The force is exerted only for 0.05 seconds since the arrow quickly moves out off the bow. And the arrow weights 0.5 Kg. From my calculations* the velocity of the arrow will be 200m/s if I'm not wrong.
But I wonder what will be the potential energy of the arrow when it's pulled in the bow?
How do we calculate it?
*Force = mass * acceleration
1 N = 1 Kg * 1m/s^2
2000 N = 0.5 Kg * a
2000 / 0.5kg = a
a = 4000m/s^2
Velocity = acceleration*time
Velocity = 4000 * 0.05s = 200m/s.
Speed of the arrow in the space is 200m/s.
The person has a bow and arrow. He stretches the arrow on the bow, and then shots the arrow out in the space. Since there are no friction and gravitational force in that space, the arrow will have constant velocity very long distance or until another force exerted on it.
But I wonder what will be the potential energy of the arrow when it's pulled in the bow?
How do we calculate it?
*Force = mass * acceleration
1 N = 1 Kg * 1m/s^2
2000 N = 0.5 Kg * a
2000 / 0.5kg = a
a = 4000m/s^2
Velocity = acceleration*time
Velocity = 4000 * 0.05s = 200m/s.
Speed of the arrow in the space is 200m/s.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: