SUMMARY
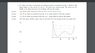
The discussion focuses on applying the conservation of energy principle to analyze a potential energy graph. The key equation utilized is F = -dU/dx, which relates force to the potential energy gradient. The participant struggles to connect the concepts of force, mass, and acceleration, specifically using F = ma and a = d²x/dt², to derive velocity at various positions on the graph. The turning point and expected motion are also critical aspects of the analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of potential energy graphs and their characteristics
- Familiarity with Newton's second law (F = ma)
- Knowledge of calculus, particularly derivatives
- Concept of conservation of energy in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the relationship between potential energy and kinetic energy in mechanical systems
- Learn how to apply the conservation of energy to solve motion problems
- Explore the concept of turning points in potential energy graphs
- Investigate the use of differential equations in analyzing motion
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and energy conservation, as well as educators seeking to clarify these concepts in a teaching context.