SUMMARY
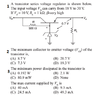
The discussion focuses on calculating power dissipation across a transistor regulator using Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). The user correctly determined the collector-emitter voltage (Vce) to be 8.7V and the emitter current (Ie) to be 9.3mA, resulting in a power dissipation of 80.91 mW. A key insight is the importance of calculating maximum power dissipation for heat sink requirements, as this is critical for ensuring the reliability of the circuit. The user concluded that the question likely contained a typo regarding minimum versus maximum power dissipation.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)
- Familiarity with transistor operation and parameters (Vce, Ie, Vbe)
- Knowledge of power dissipation calculations in electronic circuits
- Basic concepts of heat management in electronic components
NEXT STEPS
- Research maximum power dissipation calculations for transistors
- Learn about heat sink design and selection for electronic components
- Explore advanced transistor configurations for improved power handling
- Study the thermal characteristics of different transistor types
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, electronics students, and hobbyists involved in circuit design and thermal management of transistors.