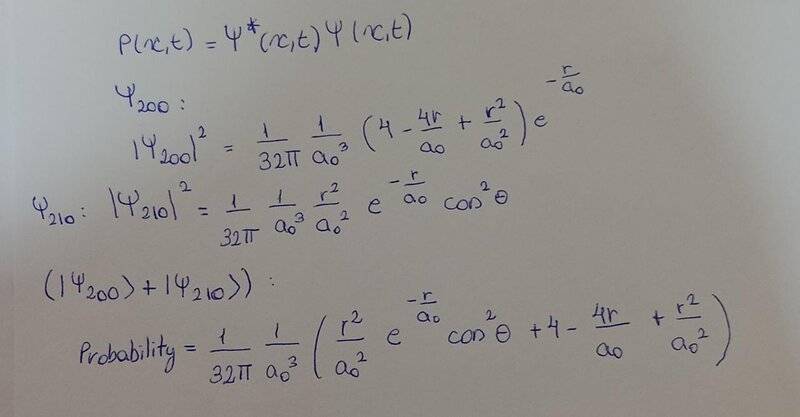Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around the probability density of the hydrogen atom, specifically focusing on the superposition of wave functions and their implications for normalization and representation in the xy-plane.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants explore the relationship between the wave functions and their squared magnitudes, questioning the correctness of their expressions. There is discussion about the normalization of the wave function and its representation in a graphical context.
Discussion Status
Some participants have provided insights regarding the normalization of wave functions and the implications of real-valued functions. Questions remain about the complexity of the results and their graphical representation, indicating an ongoing exploration of the topic.
Contextual Notes
There are references to specific guidelines for asking homework questions, emphasizing the importance of demonstrating effort in understanding the material. Additionally, there is mention of potential simplifications in the results that may not align with expectations.