Discussion Overview
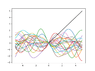
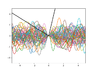
The discussion revolves around the probability of a surface realization described by a zero-mean Gaussian process exceeding a specified threshold (the black line) in a scattering problem. Participants explore the mathematical formulation of the Gaussian process and its implications for the problem at hand.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant describes the height as a zero-mean Gaussian process with a specific covariance function, seeking the probability of exceeding a threshold.
- Another participant questions the definitions of the variables involved, asking for clarification on the relationship between height and position.
- A participant clarifies that the height is modeled as a multivariate Gaussian process, explaining the covariance structure and suggesting a more common notation.
- Concerns are raised about the characterization of the process as multivariate, with a participant arguing that it is a scalar process indexed by position.
- One participant introduces the concept of Brownian Motion as a formal statement of the problem, proposing a probability expression related to the supremum of the process.
- A later reply acknowledges the introduction of Brownian Motion and suggests that the Reflection Principle may be relevant to finding a solution.
- Another participant expresses gratitude for the new perspective and discusses the potential for Monte Carlo sampling to estimate probabilities in the context of a more realistic figure.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants exhibit a mix of agreement and disagreement, particularly regarding the characterization of the Gaussian process and the interpretation of the problem. There is no consensus on the best approach to solve the probability question.
Contextual Notes
Participants express uncertainty about the definitions of variables and the implications of the covariance structure. The discussion includes unresolved questions about the nature of the Gaussian process and its application to the scattering problem.