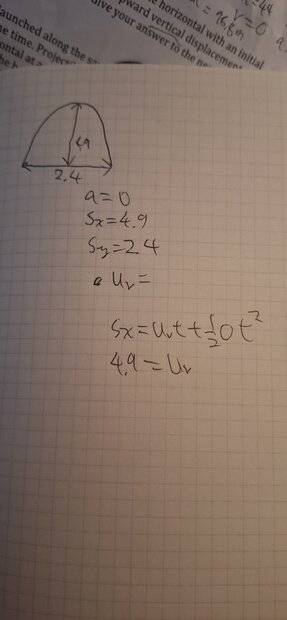Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around a projectile motion problem where the original poster seeks to determine the initial vertical speed, horizontal speed, and launch angle of a projectile, given only acceleration and distance. The context involves analyzing the motion of a ball projected upward.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the potential confusion between vertical and horizontal displacements, noting that the vertical displacement pertains to the ascent to maximum height while the horizontal displacement covers the entire trajectory. There is mention of needing to incorporate vertical acceleration into the equations.
Discussion Status
Some participants have pointed out discrepancies in the original poster's understanding of the problem setup, specifically regarding the treatment of displacements and accelerations. There is an ongoing exploration of the implications of these observations, but no consensus has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference the need for clarity on the definitions of vertical and horizontal components in the context of projectile motion. There are also indications of previous discussions on similar problems, suggesting a recurring theme in the understanding of projectile motion dynamics.
 i try to solve it but it didn't work
i try to solve it but it didn't work