Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the definition of efficiency in rocket propulsion, particularly in the context of different propulsion methods, including photon drives and traditional chemical rockets. Participants explore the implications of internal forces, momentum, and energy density in relation to thrust generation and efficiency metrics.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
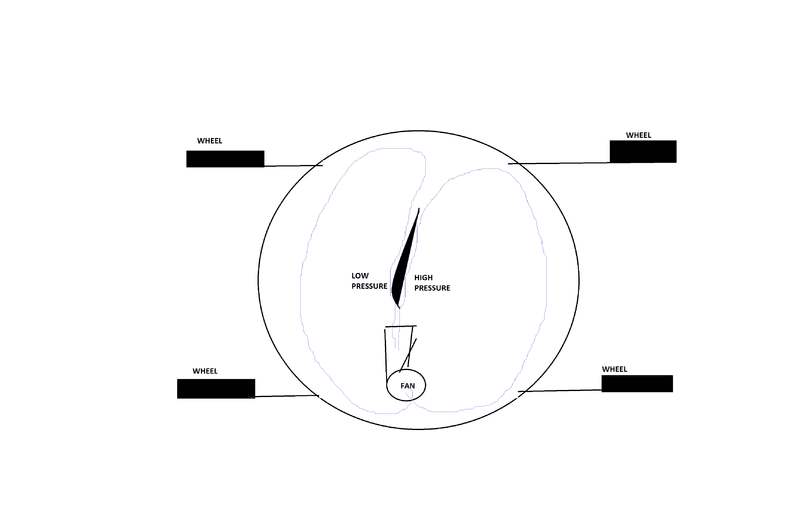
- Some participants propose that a vehicle with a closed system and internal forces, such as a fan blowing air to a wing, cannot move forward due to Newton's third law.
- Others argue that one must consider pressure distributions on all surfaces within the closed system to understand the forces at play.
- A question is raised about the feasibility of using a photon drive for propulsion in a closed system, with some noting that photons carry momentum and can affect the system's motion if they escape.
- Participants discuss the energy requirements for achieving thrust with a laser, noting that a continuous output of 3GW would be necessary for 10N of thrust.
- Some participants highlight the inefficiency of photon drives compared to chemical rockets, emphasizing the energy density of chemical fuels and the benefits of using expended fuel as reaction mass.
- There is a discussion on how efficiency can be defined in different ways, with some suggesting that thrust per unit energy is a poor measure for photon drives, while others propose that impulse per unit mass of fuel is a more relevant metric for rockets.
- Participants note that maximizing thrust from fuel often requires high exhaust velocities, which can conflict with the goal of minimizing the mass of propellant carried.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express multiple competing views on the efficiency of different propulsion methods, particularly regarding the definitions and metrics used to evaluate efficiency. The discussion remains unresolved as various perspectives on propulsion efficiency are presented without consensus.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight the complexity of defining efficiency in propulsion systems, noting that different definitions can lead to different conclusions about the effectiveness of photon drives versus chemical rockets. The discussion also touches on the implications of carrying reaction mass and energy density in propulsion efficiency.