Homework Help Overview
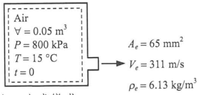
The discussion revolves around the concept of mass and volume in a system involving gas discharge. Participants are exploring the relationship between expelled air and the mass of the system, questioning how mass can remain unchanged despite air being expelled.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning the implications of mass conservation in a system where air is expelled. There are inquiries about the determination of cross-section and the validity of taking time derivatives of volume integrals. Some are also discussing the role of control volumes in this context.
Discussion Status
There is an ongoing exploration of the concepts involved, with some participants providing insights into the nature of the system and control volumes. Guidance has been offered regarding the interpretation of mass flow and the dynamics of the system, though no consensus has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating complex ideas related to fluid dynamics and control volumes, with some expressing confusion over mathematical representations and assumptions about the system boundaries.