nicknickoli
- 7
- 0
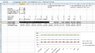
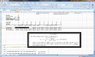
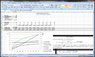
I'm using the formulas on Wikipedia and the cited Goldstone article to try and figure out how much force I'll put on climbing hardware when taking a fall. The numbers in Excel all look the same despite rope stretch?
It's relevant because with aid climbing, fall distances are very short (and with lots of rope out there's a lot absorbed in stretch) but the gear can be margional. Some aid climbing anchor pieces take less than 2kN of force.
How can I change this so rope stretch properly shows me how impact force on the climber (or anchor) changes??
It's relevant because with aid climbing, fall distances are very short (and with lots of rope out there's a lot absorbed in stretch) but the gear can be margional. Some aid climbing anchor pieces take less than 2kN of force.
How can I change this so rope stretch properly shows me how impact force on the climber (or anchor) changes??