SUMMARY
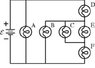
The discussion focuses on ranking the brightness of six identical bulbs (A-F) connected to an ideal battery based on their resistances. Participants emphasize the importance of calculating the currents through each bulb, particularly noting that the current in bulb D is influenced by the configurations of bulbs B, C, E, and F. To accurately determine brightness, users are advised to apply formulas for resistors in series and parallel, considering the distribution of current based on resistance values. The conversation highlights the necessity of demonstrating initial problem-solving attempts to receive further assistance.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electrical circuits and current flow
- Knowledge of resistor configurations in series and parallel
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law and resistance calculations
- Basic principles of light bulb behavior in electrical circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of current division in parallel circuits
- Learn how to calculate equivalent resistance for series and parallel combinations
- Explore the concept of negative resistance in light bulbs
- Review examples of circuit analysis involving multiple resistors
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, electrical engineering enthusiasts, and anyone interested in understanding the behavior of electrical circuits involving resistors and light bulbs.