Tony Hau
- 107
- 30
- Homework Statement
- Plot voltage(proportional to the charge density) versus the radial distance r. How does the charge density vary with position? Explain your result.
- Relevant Equations
- Q=CV
So this is a question from my lab report on capacitance.
The aim of the experiment is to find out the relationship between surface charge density and radial distance from the centre of the plate capacitor. And in this experiment I have recorded 5 sets of data, namely r=0, V=4, r=1, V=3.5, r=2, V=3, r=3, V=2, r=4, V=2.5. The error of voltage is plus or minus 0.5V.
The steps involved are as follows:
Firstly we set two circular plates coated with metals to 5 cm apart. Then we connect the a 1000V power supply across the capactior.
Secondly, we use a proof plate to measure the charge in different radial distance from the centre one of the circular plate. The radial distances are as above listed.
The function of the proof plate is that it can acquire the same amount of charge as the section of the touched surface and so you can dertermine the charge density of the sample surface.
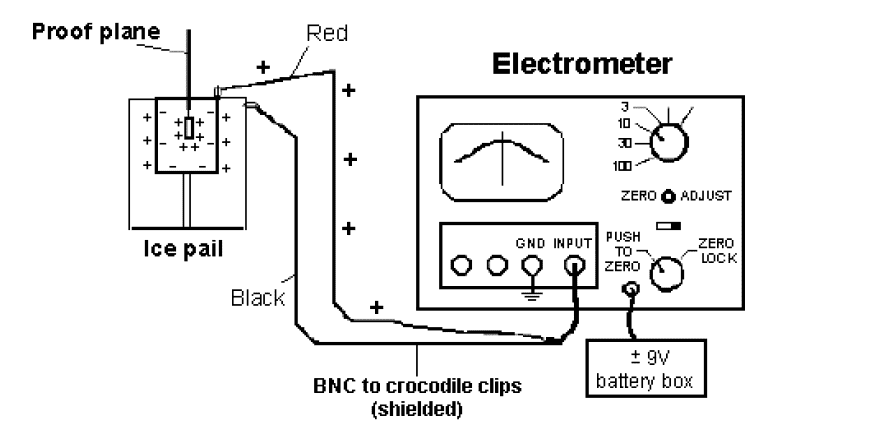
Finally, we measure the charge on proof plate by using a Faraday Ice pail with an electrometer, as shown in this picture.
What I do not understance is why the surface charge density will actually vary with the radial distance from the centre of the plate. I have been always told to assume constant surface charge density. And from my data, it seems that the surface charge density decreases as the radial distance increases.
The aim of the experiment is to find out the relationship between surface charge density and radial distance from the centre of the plate capacitor. And in this experiment I have recorded 5 sets of data, namely r=0, V=4, r=1, V=3.5, r=2, V=3, r=3, V=2, r=4, V=2.5. The error of voltage is plus or minus 0.5V.
The steps involved are as follows:
Firstly we set two circular plates coated with metals to 5 cm apart. Then we connect the a 1000V power supply across the capactior.
Secondly, we use a proof plate to measure the charge in different radial distance from the centre one of the circular plate. The radial distances are as above listed.
The function of the proof plate is that it can acquire the same amount of charge as the section of the touched surface and so you can dertermine the charge density of the sample surface.
Finally, we measure the charge on proof plate by using a Faraday Ice pail with an electrometer, as shown in this picture.
What I do not understance is why the surface charge density will actually vary with the radial distance from the centre of the plate. I have been always told to assume constant surface charge density. And from my data, it seems that the surface charge density decreases as the radial distance increases.
Last edited: