ViolentCorpse said:
ghwellsjr said:
The thin blue lines show the images of the Earth's clock as they arrive at the black body. Prior to encounter, the body sees the Earth's clock ticking much faster than its own and after encounter, much slower, even though the Time Dilation of the Earth's clock in this frame is constant throughout and at a different factor than either of the observed tick rates.
Oh wow. It never occurred to me that clocks could just as well be observed ticking faster than in the observer's inertial frame of reference. However, I don't understand the reason why the "ticking rate" is different before and after the encounter, even though the time dilation factor isn't changing?
Thank you soo much!
As jtbell pointed out, it's a Doppler effect but you need to look up the
Relativistic Doppler Effect to see the formula that works in this case and if you do you will see that the formula for the Doppler Factor is:
√((1+β)/(1-β))
which in our case for the relative speed of β=0.9 between the blue Earth and the black body is:
√((1+0.9)/(1-0.9)) = √((1.9)/(0.1)) = √19 =
4.359
This applies to the tick rate that an observer sees a remote clock coming towards him at 0.9c compared to the tick rate of his own clock. If the remote clock is moving away at the same speed, then the inverse factor applies:
1/4.359 =
0.229
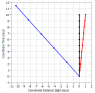
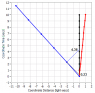
So let's see how this works. Here is another spacetime diagram similar to one I made in my previous post where the blue Earth and the black body are moving in the frame at the same speed in opposite directions (just so the diagram isn't too big):
Look at how the black body observes the ticking of the Earth's clock. Starting from about 3 seconds before encounter, the black body sees the Earth clock at 13 seconds before encounter. So the black body sees the Earth's clock ticking about 13/3 or about
4.333 times faster than its own which is very close to the actual value of
4.359.
Then after encounter, the black body sees the Earth's clock at 3 seconds when its own clock is at about 13 seconds. This is the inverse of the previous ratio or about
0.231 which is close to the actual value of
0.229.
I think in this frame you can easily see that if we drew in lines for how Earth would observe the clock of the black body, it would be symmetrical. And if you remember from my previous post, it doesn't matter which frame we transform a scenario into, all observations of any observer remain the same. So we can say that the Doppler factors that each observer makes of the others clock both during approach and retreat are identical. This is an important consequence of the first postulate of Special Relativity, that in relative inertial motion, both observers will make the same observations of the other observer.
In this frame, the Earth and the black body are both traveling at 0.6268c which determines a Time Dilation factor of 1.283 which neither observer can have any way to determine (because they don't know that we are looking at them in this frame) but if we use a frame where one of the observers is stationary, like the first one in my previous post then the Time Dilation factor at 0.9c is
2.294. There is a simple way that these two observers can calculate this value, they just average the two Doppler ratios that they determined, in this case (4.359/0.229)/2 = 4.588/2 =
2.294. But of course they would have to know this little trick.
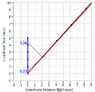
Is there a way that they can calculate what the Time Dilation of the other ones clock would be in their own rest frame and without having to pass each other? Yes, there is, as I mentioned at the end of the previous post, using a combination of radar signals and observing the other ones clock. Here is a diagram showing the measurements that the Earth makes of both the black body and the red body but in the black body's rest frame (just so we can't cheat):
Look first at the bottom of the diagram where the Earth is approaching both bodies which start out at rest with respect to each other. Earth has been making continual radar measurements of the two bodies but I only show one significant set of radar signals. Earth sent out the signal at its time of -4.36 seconds and received the echo at -0.23. Remembering the calculations from post #8, this yields a measurement time of
-2.295. (We don't care about the distance calculation.) Earth also observes that both clocks were at
-1 second when the radar reflection occurred. These numbers are the result of the first measurement.
Now Earth has to make a second measurement and for convenience, we will use the one at encounter where all the numbers are
0. (This same process will work for any other pair of measurements prior to encounter but it would take a larger diagram and twice as much calculation.)
So now Earth can determine how much time would have progressed in its own rest frame during the time that the bodies progressed. It is 0-(-2.295) or 2.295 seconds and since the bodies progress through 1 second, the Time Dilation factor is
2.295, very close to the actual
2.294.
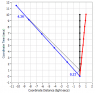
After the encounter, Earth has to make two separate measurements for the two bodies since the red one accelerated at the encounter. For the black body, the measurements are 0.23 and 4.36 for an average of
2.295, the same as before encounter. No surprise there but let's do it for the red body. The numbers are 0.21 and 4.81 for an average of
2.51 and from post #5 we determined that the speed of the red body relative to Earth is 0.917c which yields a Time Dilation factor of
2.507, a close match.