fog37
- 1,566
- 108
- TL;DR
- Reported uncertainties for time and distance in physics experiment used to create error bars in scatterplot
Hello,
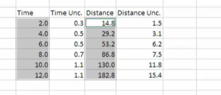
I was looking at my physics lab manual... There is a table reporting time and distance data which were both measured and collected (see below). My understanding is that the uncertainty for different and measured time instants should be the same because the time was measured with the same instrument (say a stopwatch) which determines the instrumental uncertainty. However, the 3rd column shows different uncertainty values for different ##t## values.. The manual does not explain why. Those different uncertainties could be relative uncertainties, i.e. the instrument uncertainty divided by the measured value...
Same goes for the distance: if we used a meter stick, the conservative uncertainty should be half the least count, i.e. 0.5 mm or 0.05cm. So the 4th column is the relative uncertainty.
These relative uncertainties are used to create error bars...Is that a good and standard procedure?
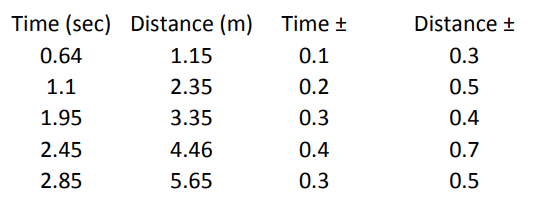
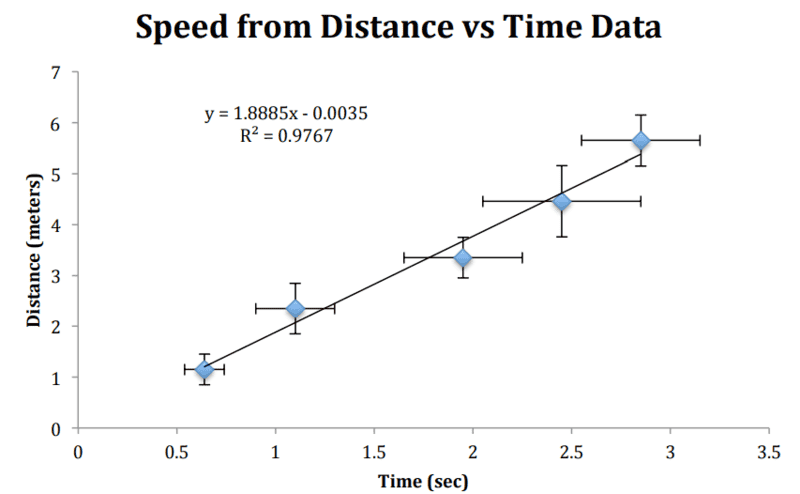
Another table I found shows uncertainties that are bigger than 1 and are different for different t values (same goes for distance). How are those uncertainties calculated?
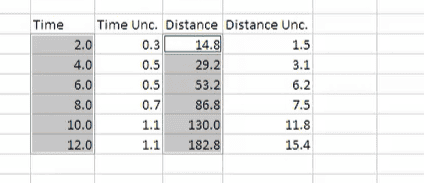
I was looking at my physics lab manual... There is a table reporting time and distance data which were both measured and collected (see below). My understanding is that the uncertainty for different and measured time instants should be the same because the time was measured with the same instrument (say a stopwatch) which determines the instrumental uncertainty. However, the 3rd column shows different uncertainty values for different ##t## values.. The manual does not explain why. Those different uncertainties could be relative uncertainties, i.e. the instrument uncertainty divided by the measured value...
Same goes for the distance: if we used a meter stick, the conservative uncertainty should be half the least count, i.e. 0.5 mm or 0.05cm. So the 4th column is the relative uncertainty.
These relative uncertainties are used to create error bars...Is that a good and standard procedure?
Another table I found shows uncertainties that are bigger than 1 and are different for different t values (same goes for distance). How are those uncertainties calculated?