karush
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,240
- 5
four-sided die has three blue face, and one red face.
The die is rolled.
B be the event blue face lies down, and R be the event a red face lands down
a Write down
i $\quad P(B)=\dfrac{3}{4}\quad$ ii $\quad P(R)=\dfrac{1}{4}$
b If the blue face lands down, the dieu is not rolled again. If the red face lands down, the die is rolled once again.
This is represented by the following tree diagram, where p, s, t are probabilities.
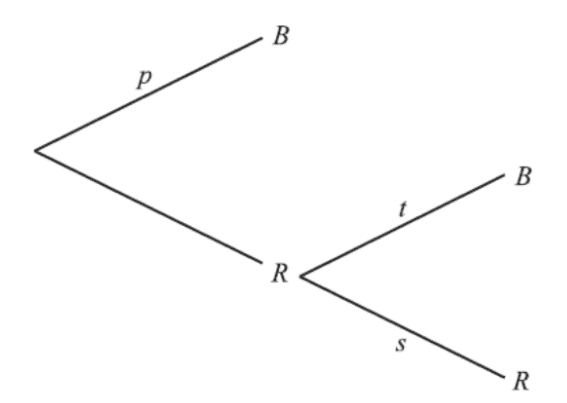
Find the value of p, of s and of t.
c Guiseppi plays a game where he rolls the die.
If a blue face lands down, he scores 2 and is finished.
If the red face lands down, he scores 1 and rolls one more time.
Let X be the total score obtained.
$ \quad \texit{ Show that } $P(X=3)=\frac{3}{16}$
[ii] Find $\quad P(X=2)$
[d i] Construct a probability distribution table for X. [5 marks]
[ii] Calculate the expected value of X.
[e] If the total score is 3, Guiseppi wins . If the total score is 2, Guiseppi gets nothing.
Guiseppi plays the game twice. Find the probability that he wins exactly .
ok I only time to do the first question so hope going in right direction
I know the answers to all this is quickly found online but I don't learn too well by C/P
The die is rolled.
B be the event blue face lies down, and R be the event a red face lands down
a Write down
i $\quad P(B)=\dfrac{3}{4}\quad$ ii $\quad P(R)=\dfrac{1}{4}$
b If the blue face lands down, the dieu is not rolled again. If the red face lands down, the die is rolled once again.
This is represented by the following tree diagram, where p, s, t are probabilities.
Find the value of p, of s and of t.
c Guiseppi plays a game where he rolls the die.
If a blue face lands down, he scores 2 and is finished.
If the red face lands down, he scores 1 and rolls one more time.
Let X be the total score obtained.
$ \quad \texit{ Show that } $P(X=3)=\frac{3}{16}$
[ii] Find $\quad P(X=2)$
[d i] Construct a probability distribution table for X. [5 marks]
[ii] Calculate the expected value of X.
[e] If the total score is 3, Guiseppi wins . If the total score is 2, Guiseppi gets nothing.
Guiseppi plays the game twice. Find the probability that he wins exactly .
ok I only time to do the first question so hope going in right direction
I know the answers to all this is quickly found online but I don't learn too well by C/P
Last edited: