Kelli Van Brunt
- 10
- 3
- Homework Statement
- A full moon occurred on June 19, 2008 at 00h 30m West Indonesian Time (local civil time for western part of Indonesia with reference to geographic longitude of 105° E). Calculate the extreme values of duration of the Moon above the horizon for observers at Bosscha Observatory (longitude: 107º 35' 00″.0 E, latitude: 6º 49' 00″.0 S, Elevation: 1300.0 m). Time zone = UT +7h 00m.
- Relevant Equations
- None; this is a conceptual question
My apologies for not detailing my attempts at a solution; I'm not sure how to to digitally illustrate or describe the various setups I attempted before looking at the solution to this problem. I am also ONLY asking about the setup, though I included the full question for context.
The solution to this problem has the following setup:
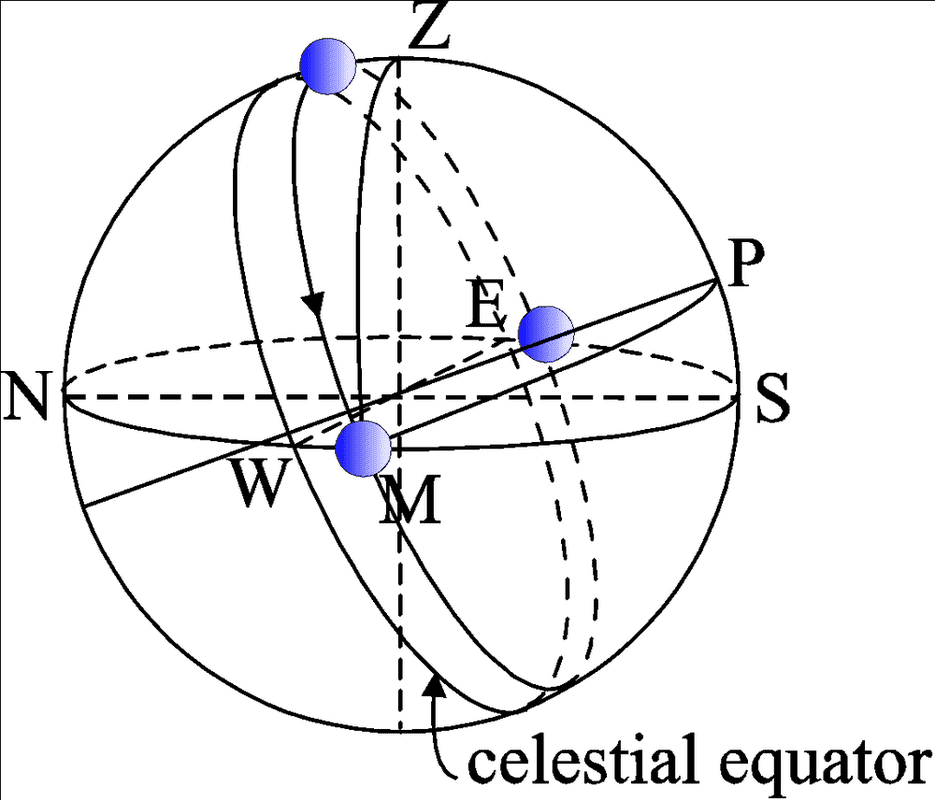
Where Z = zenith, P = south celestial pole, and M = moon (I assume represented by the path of the little blue spheres). SP is the latitude of the observing site and PM is 90º - declination of Moon. My main question is, why is P above the horizon/NESW plane when the latitude of the observing site is positive? Shouldn't an observer in the north not be able to "see" the south celestial pole? I drew a diagram of the situation in the equatorial plane below and am wondering why this is not the correct setup. The horizontal analogy to this would, I assume, be the above diagram but with the moon's path, celestial equator, and celestial south pole shifted clockwise so that M is to the right of the zenith and P is below the horizon. I apologize for my very bad graphic design skills. Can anyone clarify this for me?
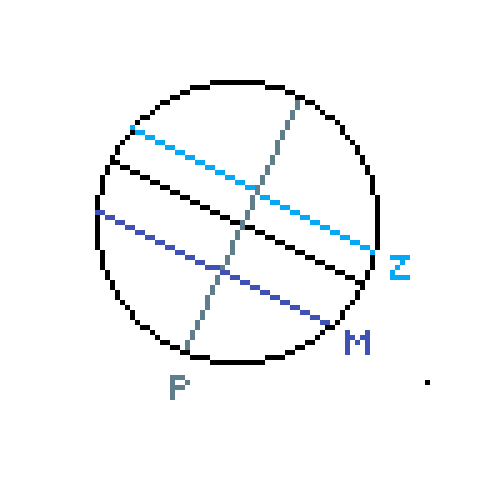
EDIT: Sorry for posting this twice - that was an accident.
The solution to this problem has the following setup:
Where Z = zenith, P = south celestial pole, and M = moon (I assume represented by the path of the little blue spheres). SP is the latitude of the observing site and PM is 90º - declination of Moon. My main question is, why is P above the horizon/NESW plane when the latitude of the observing site is positive? Shouldn't an observer in the north not be able to "see" the south celestial pole? I drew a diagram of the situation in the equatorial plane below and am wondering why this is not the correct setup. The horizontal analogy to this would, I assume, be the above diagram but with the moon's path, celestial equator, and celestial south pole shifted clockwise so that M is to the right of the zenith and P is below the horizon. I apologize for my very bad graphic design skills. Can anyone clarify this for me?
EDIT: Sorry for posting this twice - that was an accident.