SUMMARY
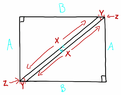
The discussion focuses on solving for the lengths X and Y and angle Z of a parallelogram situated within a rectangle measuring 15 inches in height and 20.5 inches in width. The area of the parallelogram is expressed as A_P = 1.5X, while the relationship between the rectangle's dimensions and the parallelogram is established through the equation AB = (B - Y)A + 1.5X. Utilizing Pythagorean theorem, the equation B - Y = √(X² - A²) is derived, leading to a single-variable equation for further analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic geometry concepts, specifically parallelograms and rectangles.
- Familiarity with the Pythagorean theorem and its application in solving for unknown lengths.
- Ability to manipulate algebraic equations to isolate variables.
- Knowledge of area calculations for geometric shapes.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of parallelograms and their relationship to rectangles.
- Learn how to apply the Pythagorean theorem in various geometric contexts.
- Explore algebraic techniques for solving equations with one variable.
- Investigate area formulas for different geometric shapes, including triangles and parallelograms.
USEFUL FOR
Students, educators, and professionals in mathematics or engineering fields who require a deeper understanding of geometric relationships and algebraic problem-solving techniques.