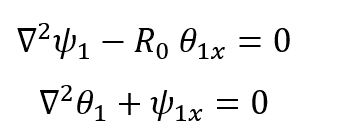SUMMARY
This discussion focuses on solving a system of two partial differential equations (PDEs) related to hydrodynamic stability. Participants emphasize that there are no universal methods for solving all PDE systems, and they highlight the importance of boundary conditions and the correct formulation of the problem. The suggested approach involves using normal modes and linear stability analysis, specifically substituting functions of the form (\theta, \psi) = (\Theta e^{k_nx}\sin(n\pi y), \Psi e^{k_nx}\sin(n\pi y)). The solution requires determining the eigenvalues from a generalized eigenvalue problem defined by the matrix M(k_n).
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
- Familiarity with linear stability analysis techniques
- Knowledge of boundary conditions in fluid dynamics
- Experience with eigenvalue problems and matrix theory
NEXT STEPS
- Study the method of normal modes in the context of PDEs
- Learn about linear stability analysis in fluid dynamics
- Explore generalized eigenvalue problems and their applications
- Research boundary condition types such as no-slip and stress-free conditions
USEFUL FOR
Researchers, mathematicians, and engineers working in fluid dynamics, particularly those dealing with stability analysis of hydrodynamic systems and partial differential equations.