SUMMARY
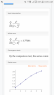
The forum discussion centers on finding the sum of the series from n=1 to infinity of n^2/(2+1/n)^n. Participants clarify the expression as n^2/(2^n(1 + 1/(2n))^n) and discuss convergence tests. A partial sum of approximately 3.77 is calculated by summing the first 25 terms using Excel. The conversation highlights the need for a method to derive the exact sum, with suggestions including exploring similar examples and integral equations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of infinite series and convergence tests
- Familiarity with mathematical notation and expressions
- Experience with numerical methods for approximating series sums
- Basic knowledge of calculus and functions
NEXT STEPS
- Research convergence tests for series, such as the Ratio Test and Root Test
- Explore numerical methods for estimating series sums, including partial sums
- Investigate integral equations related to series, particularly in the context of generating functions
- Study examples of similar series in advanced calculus textbooks
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those focusing on series convergence and summation techniques, as well as anyone interested in numerical analysis and approximation methods.