Math Amateur
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,920
- 48
- TL;DR
- I need help in order to fully understand the order topology ... so I present a very simple example ...
I am reading Tej Bahadur Singh: Elements of Topology, CRC Press, 2013 ... ... and am currently focused on Chapter 1, Section 1.4: Basis ... ...
I need help in order to fully understand the order topology ... and specifically Example 1.4.4 ... ...Example 1.4.4 reads as follows:
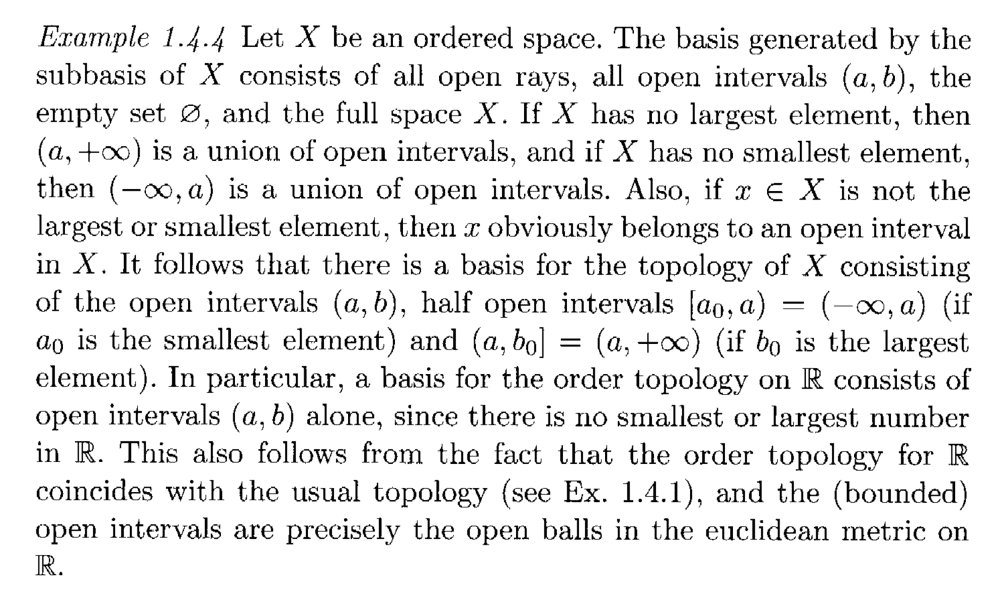
In order to fully understand Example 1.4.4 I decided to take ##X = \{ a, b, c \}## where ##a \leq b, a \leq c## and ##b \leq c## ... ...Now in the above text, Singh writes the following:
" ... ... The basis generated by the subbasis of ##X## consists of all open rays, all open intervals ##(a, b)##, the emptyset ##\emptyset##, and the full space ##X##. ... ... "Now as I understand it the open rays in ##X## are as follows:
##( - \infty, a) = \emptyset##
##( - \infty, b) = \{ a \}##
##( - \infty, c) = \{ a, b \}##
##( a, \infty) = \{ b, c \}##
##( b, \infty) = \{ c \}##
##( c, \infty) = \emptyset##... and (see definition of order topology below) the open rays constitute the subbasis of the order topology ...To generate the basis, according to the text of Example 1.4.4, we have to add in all open intervals ##(a, b)##, the emptyset ##\emptyset##, and the full space ##X##. ... ...
The open intervals in ##X## are as follows:
##(a, b) = \emptyset##
##(b, c) = \emptyset##
##(a, c) = \{ b \}##The above open rays, open intervals together with ##\emptyset## (already in the basis) and ##X## constitute a basis for the order topology of the ordered set ##X## ... ...Can someone please confirm that the above analysis is correct and/or point out errors or shortcomings ... ..
Help will be much appreciated ... ...
Peter======================================================================================It may help Physics Forum readers of the above post to have access to Singh's definitions of the order topology, together with the definitions of subbasis and basis ... so I am providing the same ... as follows:
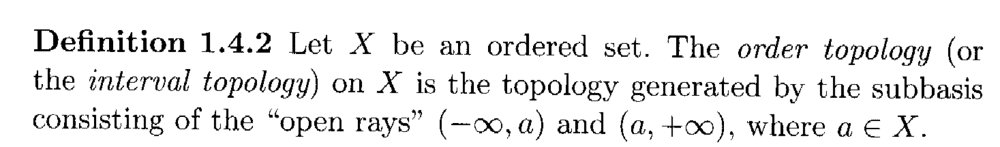
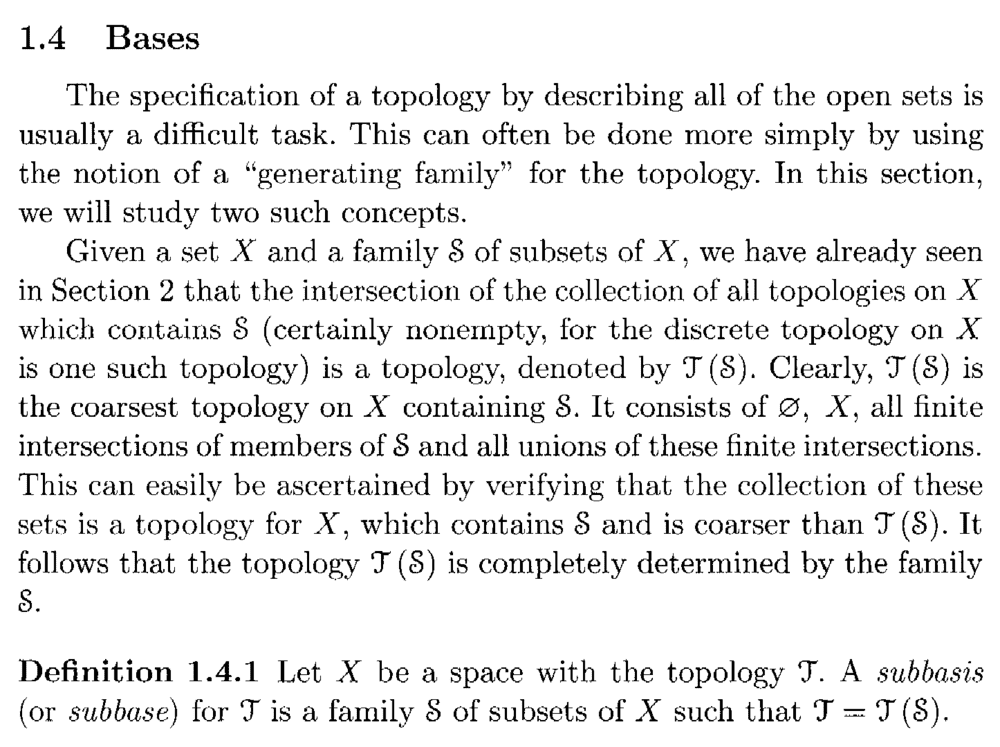
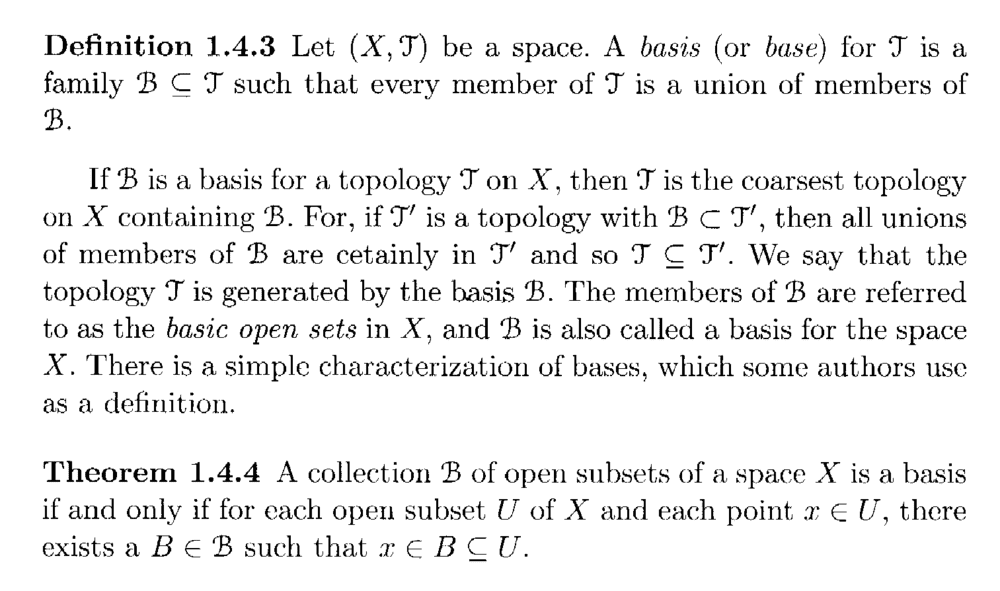 Hope that helps ... ...
Hope that helps ... ...
Peter
I need help in order to fully understand the order topology ... and specifically Example 1.4.4 ... ...Example 1.4.4 reads as follows:
In order to fully understand Example 1.4.4 I decided to take ##X = \{ a, b, c \}## where ##a \leq b, a \leq c## and ##b \leq c## ... ...Now in the above text, Singh writes the following:
" ... ... The basis generated by the subbasis of ##X## consists of all open rays, all open intervals ##(a, b)##, the emptyset ##\emptyset##, and the full space ##X##. ... ... "Now as I understand it the open rays in ##X## are as follows:
##( - \infty, a) = \emptyset##
##( - \infty, b) = \{ a \}##
##( - \infty, c) = \{ a, b \}##
##( a, \infty) = \{ b, c \}##
##( b, \infty) = \{ c \}##
##( c, \infty) = \emptyset##... and (see definition of order topology below) the open rays constitute the subbasis of the order topology ...To generate the basis, according to the text of Example 1.4.4, we have to add in all open intervals ##(a, b)##, the emptyset ##\emptyset##, and the full space ##X##. ... ...
The open intervals in ##X## are as follows:
##(a, b) = \emptyset##
##(b, c) = \emptyset##
##(a, c) = \{ b \}##The above open rays, open intervals together with ##\emptyset## (already in the basis) and ##X## constitute a basis for the order topology of the ordered set ##X## ... ...Can someone please confirm that the above analysis is correct and/or point out errors or shortcomings ... ..
Help will be much appreciated ... ...
Peter======================================================================================It may help Physics Forum readers of the above post to have access to Singh's definitions of the order topology, together with the definitions of subbasis and basis ... so I am providing the same ... as follows:
Peter