- #1
TS656577
- 62
- 0
Homework Statement
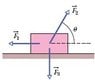
The figure shows three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by 2.8 m over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 = 5.5 N, F2 = 8.7 N, and F3 = 2.6 N, and the indicated angle is θ = 60°. (a) During the displacement, what is the net work done on the trunk by the three applied forces, the gravitational force, and the normal force? (b) Is there a net transfer of energy to or from the trunk? (c) Does the kinetic energy of the trunk increase or decrease?
Homework Equations
W=Fd
The Attempt at a Solution
I know that Force 1 did 15.4 J of work (5.5 times 2.8) and I know that Force 2 did -12.18J of work (dotted line = 4.35 and 4.35 times 2.8= 12.18) Force 3 didnt do any work on the block. I don't know how to tie it all together
D
 .
.