- #1
shin777
- 42
- 0
Three forces -- in equilibrium or not?
Hi. I am new to physics and need some help on this question asap. Did I get it right or is it wrong? Correct me if I am wrong. Thank you.
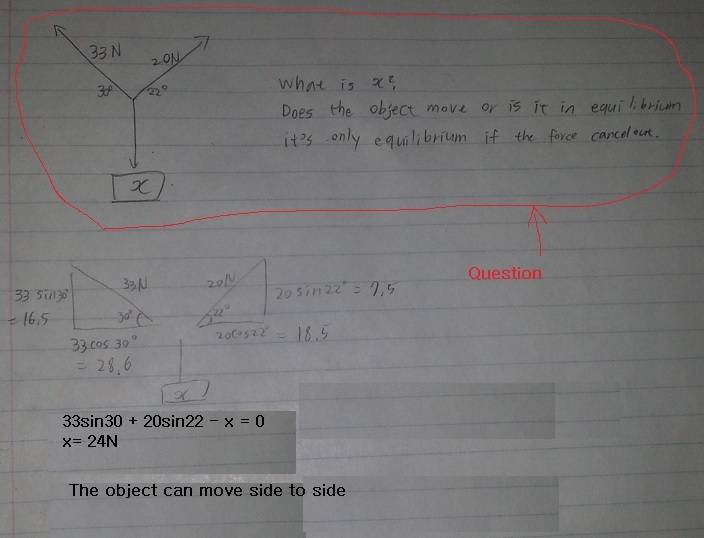
Hi. I am new to physics and need some help on this question asap. Did I get it right or is it wrong? Correct me if I am wrong. Thank you.