SUMMARY
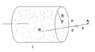
The discussion focuses on calculating the total force exerted by n particles within a cylindrical container of radius R and height l towards a point A. The force from each particle is defined by the equation f = K/d², where K is a constant and d represents the distance from the particle to point A. The participants emphasize the necessity of using integration to derive the total force, considering that the height (h) remains constant. A visual attachment was referenced to aid in understanding the spatial arrangement of the particles.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic physics concepts, specifically force and distance calculations.
- Familiarity with integration techniques in calculus.
- Knowledge of cylindrical coordinates for spatial analysis.
- Experience with mathematical modeling of physical systems.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of force calculations in physics, focusing on inverse square laws.
- Learn about integration methods applicable to multi-variable functions.
- Explore cylindrical coordinate systems and their applications in physics.
- Investigate mathematical modeling techniques for particle interactions in confined spaces.
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, mathematicians, and engineers involved in particle dynamics and force calculations in confined geometries.