OMG_Physics
- 5
- 2
Thread moved from a technical forum, so homework template missing
TL;DR:
My professor asked me to graph the probability that a particle would be excited from the ground state to a stationary state with a certain energy E (y-axis) verse the energy of that new state (x-axis). I need help finding this probability as a function of E.
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
P is the momentum operator.
Why does this formula work? Why is it the momentum operator? How to I produce this graph?
BACKGROUND:
This is not homework! It is just supposed to be a problem to introduce some ideas (which makes me feel worse).
I have been independently study quantum mechanics for about 2 months and the professor had asked for the graph of the probability of exciting a particle (from ground state) into a scattering state with energy E with a single delta potential at the origin (please see the red line in the graph poorly drawn graph below).
The professor (without much explanation) said the way to calculate this probability is:
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
P is the momentum operator.
I was able to find the equation and produce the graph. Then he asked for the same process for the potentials below: find the probability of the particle transitioning from the ground state to an excited stationary state ΨE.
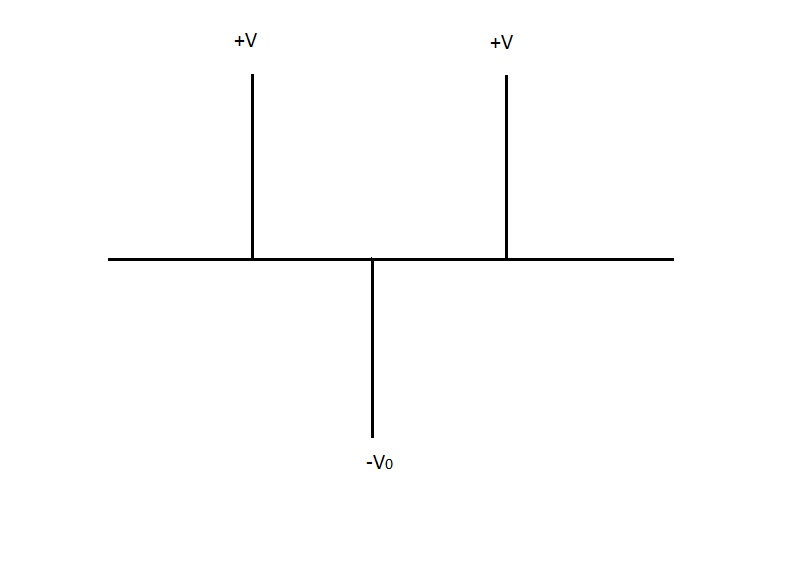
The potential is described:
V(x)=Vδ(x+a)+Vδ(x-a)-V0δ(x)
This is supposed to be how the graph looks (I'm sorry its terrible I have to hand draw it).
The red line is the probability of a particle in the ground state being excited with single negative delta potential.
The black is supposed to be describing the above (3-delta) situation.

I assumed the stationary states would be the same as a particle trapped in the well; sinusoidal with discrete energies. This doesn't produce the graph though.
Why does this formula work?
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
As you can tell I'm being a little ambiguous about the question I'm asking which is where I'm hoping this forum will come in. I'm not looking for a solution just a direction!
What should I be looking for? I can't find anything helpful in the material I've been going through. At this point I've wasted 20+ hours on this single problem and it's causing me to fall being in my actual classes.
Books I'm reading include:
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (2nd Edition): David J. Griffiths
Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 2nd Edition: R. Shankar
Quantum Mechanics, Vol. 1: Claude Cohen-Tannoudji
I've also gone through several video lectures from universities:
all of Modern Quantum Mechanics and Advanced Quantum Mechanics from Susskind and some of Adams (MIT).
So sorry for the length and if this post is formatted poorly for this forum. I did go through some of the help and things but this is my first one! I know the images are ugly.
My professor asked me to graph the probability that a particle would be excited from the ground state to a stationary state with a certain energy E (y-axis) verse the energy of that new state (x-axis). I need help finding this probability as a function of E.
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
P is the momentum operator.
Why does this formula work? Why is it the momentum operator? How to I produce this graph?
BACKGROUND:
This is not homework! It is just supposed to be a problem to introduce some ideas (which makes me feel worse).
I have been independently study quantum mechanics for about 2 months and the professor had asked for the graph of the probability of exciting a particle (from ground state) into a scattering state with energy E with a single delta potential at the origin (please see the red line in the graph poorly drawn graph below).
The professor (without much explanation) said the way to calculate this probability is:
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
P is the momentum operator.
I was able to find the equation and produce the graph. Then he asked for the same process for the potentials below: find the probability of the particle transitioning from the ground state to an excited stationary state ΨE.
The potential is described:
V(x)=Vδ(x+a)+Vδ(x-a)-V0δ(x)
This is supposed to be how the graph looks (I'm sorry its terrible I have to hand draw it).
The red line is the probability of a particle in the ground state being excited with single negative delta potential.
The black is supposed to be describing the above (3-delta) situation.
I assumed the stationary states would be the same as a particle trapped in the well; sinusoidal with discrete energies. This doesn't produce the graph though.
Why does this formula work?
Probability=|<ΨE|P|Ψg>|2
As you can tell I'm being a little ambiguous about the question I'm asking which is where I'm hoping this forum will come in. I'm not looking for a solution just a direction!
What should I be looking for? I can't find anything helpful in the material I've been going through. At this point I've wasted 20+ hours on this single problem and it's causing me to fall being in my actual classes.
Books I'm reading include:
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (2nd Edition): David J. Griffiths
Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 2nd Edition: R. Shankar
Quantum Mechanics, Vol. 1: Claude Cohen-Tannoudji
I've also gone through several video lectures from universities:
all of Modern Quantum Mechanics and Advanced Quantum Mechanics from Susskind and some of Adams (MIT).
So sorry for the length and if this post is formatted poorly for this forum. I did go through some of the help and things but this is my first one! I know the images are ugly.