- #1
keyzan
- 17
- 6
TL;DR Summary: A particle of mass m, placed in an infinite rectangular one-dimensional potential well that confines it in the segment between x=-a/2 and x=a/2
Hi guys, I need help with this exercise which reads: a particle of mass m, placed in an infinite rectangular one-dimensional potential well that confines it in the segment between x=-a/2 and x=a/2, is in the state :
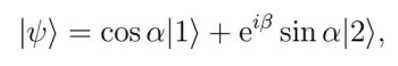
being |1> and |2> normalized kets representative of the ground state and the first excited one.
1. Determine the possible outcomes of an energy measurement and the related probabilities as a function of the real alpha and beta parameters.
Solution:
I applied the fourth postulate in the specific case with discrete eigenvalues and without degeneracy. I got:
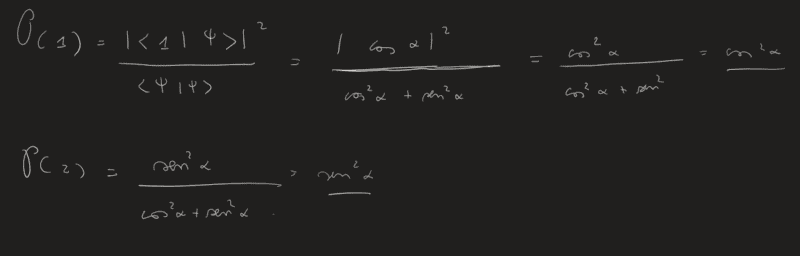
it's right?
2. Determine the average value of the impulse as the parameters vary.
Solution:
In this case I don't really know how to proceed and in general in these cases I don't know how to proceed (when it comes to average values in general). I found:
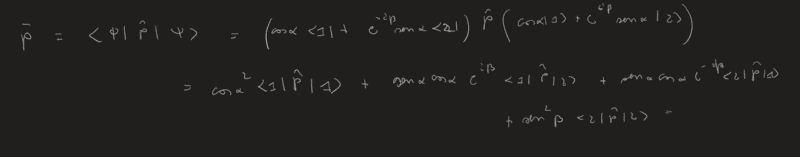
At this point I should consider that the impulse p=(h/2*pi)*k. And since I know k of the different eigenstates I can find:
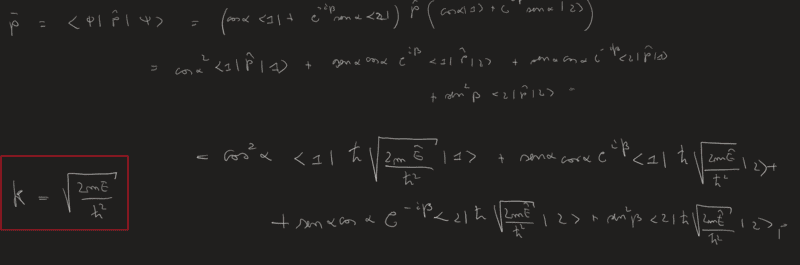
And continue in this way? But my reasoning seems very forced, I don't know. I'm doing it wrong?
Hi guys, I need help with this exercise which reads: a particle of mass m, placed in an infinite rectangular one-dimensional potential well that confines it in the segment between x=-a/2 and x=a/2, is in the state :
being |1> and |2> normalized kets representative of the ground state and the first excited one.
1. Determine the possible outcomes of an energy measurement and the related probabilities as a function of the real alpha and beta parameters.
Solution:
I applied the fourth postulate in the specific case with discrete eigenvalues and without degeneracy. I got:
it's right?
2. Determine the average value of the impulse as the parameters vary.
Solution:
In this case I don't really know how to proceed and in general in these cases I don't know how to proceed (when it comes to average values in general). I found:
At this point I should consider that the impulse p=(h/2*pi)*k. And since I know k of the different eigenstates I can find:
And continue in this way? But my reasoning seems very forced, I don't know. I'm doing it wrong?