SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on obtaining a second-order ordinary differential equation (ODE) through implicit differentiation. Participants suggest an alternative approach by isolating dy/dx and solving algebraically, leading to a separable equation. The correct formulation of dy/dx is provided as ##\frac {dy}{dx} = \frac{y^{1/2}(1 - y^{1/2} - y)}{y^{1/2}(y^{-1/2} + 1 - y)}##. The conversation emphasizes clarity in terminology, particularly the distinction between "2nd ODE" and "second-order differential equation."
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
- Familiarity with implicit differentiation techniques
- Knowledge of algebraic manipulation of equations
- Ability to identify separable differential equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the method of implicit differentiation in detail
- Learn about separable differential equations and their solutions
- Explore the conversion of higher-order ODEs to systems of first-order ODEs
- Investigate the role of coefficients in differential equations and their impact on solutions
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, physics students, and anyone involved in solving differential equations, particularly those interested in transitioning from second-order to first-order systems.
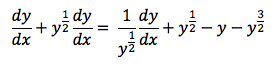
 Isn't it just dy/dx = - y. ?
Isn't it just dy/dx = - y. ?