- #1
jisbon
- 476
- 30
- Homework Statement
- Give an expression for the induced current in a homopolar generator as a function of angular velocity ##\omega##
- Relevant Equations
- -
So I was searching up on the homopolar generator and found this explanation for the generator, as well as the proposed solution.
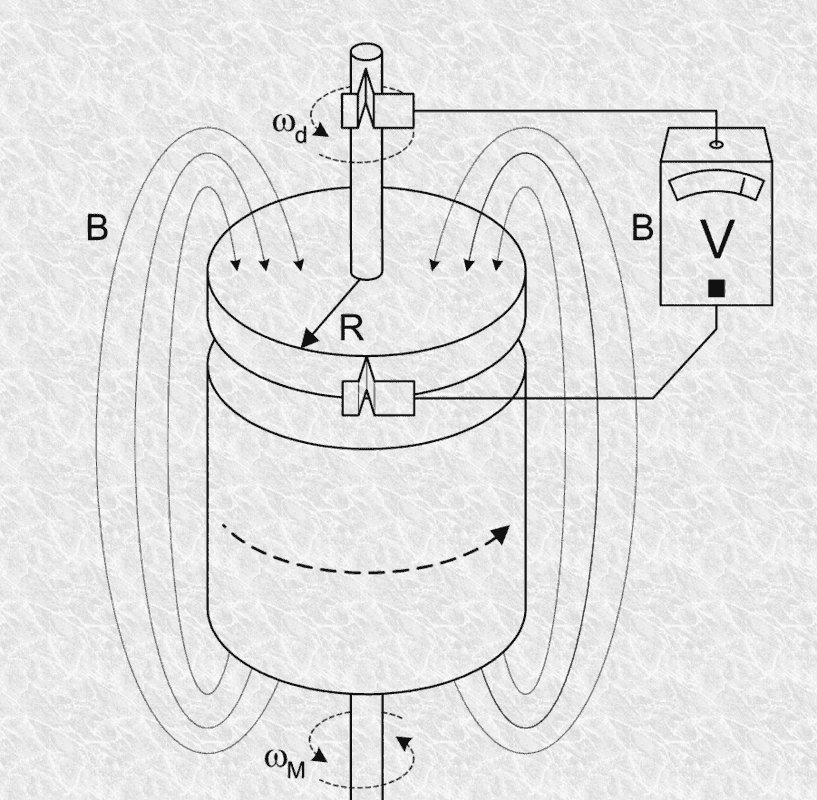
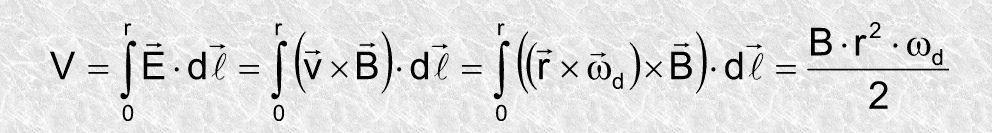
However, I don't really understand what the solution is trying to do here.
Ok, I understand to find the current, you will need the potential, which is the integration of emf. However, I'm stuck at the last part. How did they exactly derive ##dl ##and what is ##dl## exactly?
Any explanation will be appreciated. Thanks
However, I don't really understand what the solution is trying to do here.
Ok, I understand to find the current, you will need the potential, which is the integration of emf. However, I'm stuck at the last part. How did they exactly derive ##dl ##and what is ##dl## exactly?
Any explanation will be appreciated. Thanks