d-rock
- 14
- 0
Homework Statement
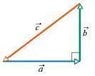
For the vectors in the figure below, with a = 8, b = 7, c = sqrt(113), give the magnitude and direction of the following cross products.
(See attachment for figure/right triangle).
(a) a x b
(b) a x c
(c) b x c
Homework Equations
\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = ABcos(\Theta)
\vec{C} = ABsin(\Theta)
The Attempt at a Solution
(a) For part one, I was able to do the Cross Product since they gave the magnitudes A and B and in the figure, vectors A and B are straight lines which means the magnitude is also the X or Y (depending on the direction).
So, I did the Cross Product and got 56k, with it coming out of the computer screen.
Now, for the last two, I have no real clue how to do this. We just learned Cross Products today and haven't gone in-depth, and I've read the book on it but it does not help. Take note I am in a college-level/duel-enrollment level course which I'm in high school, and have had no background with physics before.
Can anyone just help me on how to figure out the X and Y of vector C? That's most likely why I think I keep getting this wrong.