SUMMARY
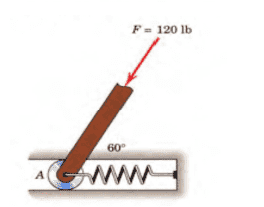
The discussion centers on calculating the spring force required to achieve a vertical resultant force in a spring mechanism. The participants determined that a compressive force of 60N is necessary, with a resultant force calculated as 10800. The calculations involve vector addition, specifically using the equation R=F2+Fx2-2(F)(Fx)cos120, leading to a resultant magnitude of approximately 103.92. The conversation also clarifies the conditions under which the spring is in tension or compression based on the direction of the applied forces.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vector addition and components
- Familiarity with spring mechanics and force types (tensile and compressive)
- Knowledge of trigonometric functions in force resolution
- Ability to perform calculations involving resultant forces
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of static equilibrium in mechanical systems
- Learn about vector resolution techniques in physics
- Explore the applications of Hooke's Law in spring mechanics
- Investigate the effects of angle on force components in spring systems
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in analyzing spring mechanisms and force interactions in mechanical systems.