- #1
barryj
- 854
- 51
Homework Statement
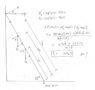
A 20 kg ladder rests against a smooth wall as shown. If a painter (50 kg) climbs 4.0 meters up a 6 meter long ladder, find the force, F1, the wall exerts on the ladder. The angle between the ladder and the ground is 53 deg.
Homework Equations
CW torque must = CCW torque
The Attempt at a Solution
The teacher posted an answer of 280 but I get 320. I think I have solved the problem correctly.
See my attached diagram