Tung Jian Seng
- 16
- 3
- TL;DR
- I wanna know how to calculate to select the right motor for my cam mechanism
Hi guys, I'm a 2nd year mechanical engineering student here. I'm currently exploring the cam mechanism and I find it interesting. But when I see the videos, I have some questions that came up in my mind. Here is the illustration below..
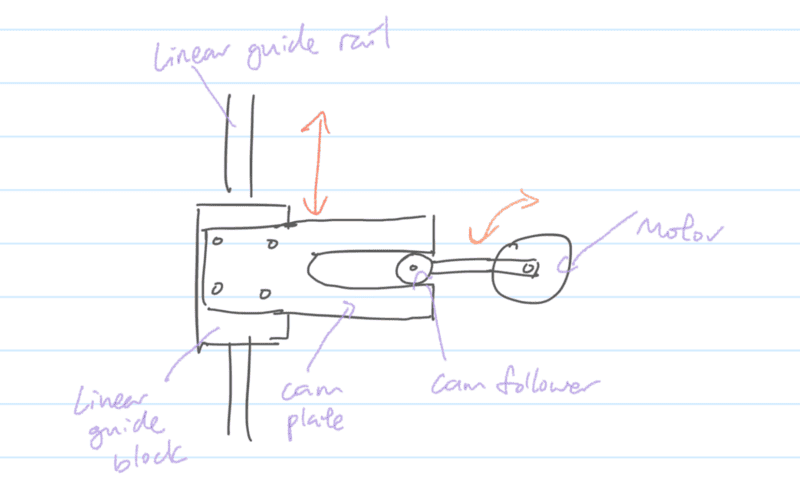
This is a top view. In this case, the cam plate is mounted on a linear guide block, and the block is driven by the motor, when the motor rotates, the block will be moving forward and backward. So here are the questions below:
1. How should I know if my motor is suitable or not?
2. It would depend on the mass of the cam plate which is the load to the motor right?
3. Is it correct that when the motor is rotating, it actually doesn't have to withstand the load of the cam plate as it is already on a frictionless slider?
4. I think what matters to the motor is the inertia force caused by the mass of the cam plate and linear guide block, but how can I calculate it to select the right motor for my application?
I would really appreciate it if someone could help to clear my doubt
Thank you in advance!
This is a top view. In this case, the cam plate is mounted on a linear guide block, and the block is driven by the motor, when the motor rotates, the block will be moving forward and backward. So here are the questions below:
1. How should I know if my motor is suitable or not?
2. It would depend on the mass of the cam plate which is the load to the motor right?
3. Is it correct that when the motor is rotating, it actually doesn't have to withstand the load of the cam plate as it is already on a frictionless slider?
4. I think what matters to the motor is the inertia force caused by the mass of the cam plate and linear guide block, but how can I calculate it to select the right motor for my application?
I would really appreciate it if someone could help to clear my doubt
Thank you in advance!