ninevolt
- 21
- 0
I am having trouble understanding what exactly Bragg planes are physically.
I understand how they behave, in that they act like mirrors and reflect matter waves, but what exactly is the wave bouncing off of?
for instance
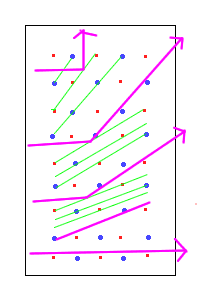
I can guarantee any physics textbook always has a picture like this, with the light bouncing off of what it seems to be nothing physical, not an atom, just the Bragg plane. I am really having trouble swallowing what exactly causes the Bragg plane. Or is it something that we just accept like electrons not emitting radiation in atoms even though they seem to be accelerating?
I understand how they behave, in that they act like mirrors and reflect matter waves, but what exactly is the wave bouncing off of?
for instance
I can guarantee any physics textbook always has a picture like this, with the light bouncing off of what it seems to be nothing physical, not an atom, just the Bragg plane. I am really having trouble swallowing what exactly causes the Bragg plane. Or is it something that we just accept like electrons not emitting radiation in atoms even though they seem to be accelerating?